-
Subscribe to Blog:
SEARCH THE BLOG
CATEGORIES
- Aerospace
- Asset Maintenance
- Automotive
- Blog
- Building Products
- Case Studies
- Chemical Processing
- Consulting
- Food & Beverage
- Forestry Products
- Hospitals & Healthcare
- Knowledge Transfer
- Lean Manufacturing
- Life Sciences
- Logistics
- Manufacturing
- Material Utilization
- Metals
- Mining
- News
- Office Politics
- Oil & Gas
- Plastics
- Private Equity
- Process Improvement
- Project Management
- Spend Management
- Supply Chain
- Uncategorized
- Utilities
- Whitepapers
BLOG ARCHIVES
- September 2025 (1)
- August 2025 (2)
- July 2025 (2)
- June 2025 (4)
- May 2025 (1)
- April 2025 (1)
- March 2025 (1)
- February 2025 (4)
- January 2025 (4)
- December 2024 (4)
- November 2024 (2)
- October 2024 (6)
- September 2024 (5)
- August 2024 (5)
- July 2024 (6)
- June 2024 (3)
- May 2024 (3)
- April 2024 (4)
- March 2024 (3)
- February 2024 (4)
- January 2024 (5)
- December 2023 (2)
- November 2023 (1)
- October 2023 (6)
- September 2023 (3)
- August 2023 (4)
- July 2023 (2)
- June 2023 (3)
- May 2023 (7)
- April 2023 (3)
- March 2023 (3)
- February 2023 (5)
- January 2023 (6)
- December 2022 (2)
- November 2022 (5)
- October 2022 (5)
- September 2022 (5)
- August 2022 (6)
- July 2022 (3)
- June 2022 (4)
- May 2022 (5)
- April 2022 (3)
- March 2022 (5)
- February 2022 (4)
- January 2022 (7)
- December 2021 (3)
- November 2021 (5)
- October 2021 (3)
- September 2021 (2)
- August 2021 (6)
- July 2021 (2)
- June 2021 (10)
- May 2021 (4)
- April 2021 (5)
- March 2021 (5)
- February 2021 (3)
- January 2021 (4)
- December 2020 (3)
- November 2020 (3)
- October 2020 (3)
- September 2020 (3)
- August 2020 (4)
- July 2020 (3)
- June 2020 (5)
- May 2020 (3)
- April 2020 (3)
- March 2020 (4)
- February 2020 (4)
- January 2020 (4)
- December 2019 (3)
- November 2019 (2)
- October 2019 (4)
- September 2019 (2)
- August 2019 (4)
- July 2019 (3)
- June 2019 (4)
- May 2019 (2)
- April 2019 (4)
- March 2019 (4)
- February 2019 (5)
- January 2019 (5)
- December 2018 (2)
- November 2018 (2)
- October 2018 (5)
- September 2018 (4)
- August 2018 (3)
- July 2018 (2)
- June 2018 (4)
- May 2018 (3)
- April 2018 (3)
- March 2018 (2)
- February 2018 (2)
- January 2018 (1)
- December 2017 (1)
- November 2017 (2)
- October 2017 (2)
- September 2017 (1)
- August 2017 (2)
- July 2017 (2)
- June 2017 (1)
- April 2017 (3)
- March 2017 (3)
- February 2017 (2)
- January 2017 (2)
- December 2016 (2)
- November 2016 (4)
- October 2016 (4)
- September 2016 (3)
- August 2016 (6)
- July 2016 (4)
- June 2016 (4)
- May 2016 (1)
- April 2016 (3)
- March 2016 (4)
- February 2016 (2)
- January 2016 (4)
- December 2015 (3)
- November 2015 (3)
- October 2015 (1)
- September 2015 (1)
- August 2015 (4)
- July 2015 (6)
- June 2015 (4)
- May 2015 (7)
- April 2015 (6)
- March 2015 (6)
- February 2015 (4)
- January 2015 (3)
CONNECT WITH US
Tag Archives: Worker Safety
The manufacturing industry keeps society ticking, but it consists of people. As technology advances, using it to improve worker safety reigns paramount, protecting the individuals who move the machines that create the products society uses daily. Keeping abreast of the latest developments to improve industrial health and safety helps owners and managers improve working conditions and processes.
Such improvements span every aspect of the industrial process, from producing the products to warehousing them and delivering them to customers. Responsible parties can draw inspiration from the innovations below to improve industrial hygiene and safety for a healthier and happier workforce.
Warehousing Procedures
Warehouses combine multiple workers and machines in a single small space, increasing the risk of accidents. Injuries can result from equipment misuse, failure to follow safety procedures or overuse stemming from repetitive motions. For example, approximately half of all workers at certain warehouses experience an injury within their first three years. Facilities have begun to implement the following innovations to decrease accident risk.
1. Warehouse Management Systems
These advanced computer programs boost efficiency by optimizing travel routes and times to streamline picking and putting away procedures. They can prevent “traffic jams” in aisles and decrease fall risk by keeping moving equipment like forklifts out of areas where workers are using ladders or scaffolding.
2. Robotics
Robots reduce repetitive motion injuries by taking some of the heavy lifting off human hands. Additionally, they can reduce fall risk by retrieving items on high shelves. Such technology also empowers warehouse managers to make better use of vertical space instead of increasing their facility’s footprint.
3. Appropriate Safety Gear
Relying on workers to supply PPE can result in the most vulnerable going without or investing in inferior protection to meet company requirements. Providing gloves, facial protection, hearing protection, steel-toed boots and reflective vests protects workers against sudden traumatic injuries while reducing some of the wear and tear of daily work on their physical selves.
Lockout/Tagout
Lockout/tagout procedures protect against electrocution and other traumatic events, such as crushing injuries when a piece of equipment goes down and multiple workers must coordinate their efforts to correct the problem. OSHA guidelines cover proper measures for controlling energy from electrical, mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, chemical and thermal sources. Compliance with these standards saves an estimated 120 lives yearly.
Here, too, technological improvements enhance worker safety. For example, video surveillance ensures workers apply the appropriate lockout devices to equipment before service work begins. Sensors can alert workers to energy remaining trapped in the system or sound the alarm if a stray body part enters the restricted area. Improved equipment testing ensures refurbished equipment meets lockout regulation standards before operators put it to use.
Heavy Equipment
Improvements in heavy equipment also increase safety in industrial environments. Electric forklifts produce fewer emissions than previous models, sparing workers’ lungs, and their narrower bodies and smaller turning radius prevent accidental collisions in crowded warehouses. They’re also quieter, reducing noise pollution. Approximately 18% of industrial workers have a hearing impairment, which lowers their life quality and may increase dementia risk.
Forklifts aren’t the only heavy equipment going electric. Many facilities have begun to outfit their organization with full electric fleets, and even bulldozers are joining this technical revolution. Electric vehicles typically have less complicated engines, leading to fewer malfunctions and opportunities for injuries to occur as crews scramble to find workarounds.
Fall Prevention
Falls from heights are the number one cause of workplace death in the UK and lag behind only transportation and workplace violence in the United States. The term “fall from height” is somewhat misleading, as many of the fatalities involved falls from lower levels, not towering skyscraper beams.
Improved safety technology and procedures work in tandem to prevent falls. For example, requiring harnesses for work involving ladders and scaffolding can reduce the risk of injury if the standing structure falls or an accidental bump sends it tumbling. Providing additional training is another safeguard, as advances in computer technology allow workers to remediate as needed instead of waiting for a single group training to refresh their knowledge.
Worker State of Mind
Improvements in technology won’t go as far as they can in increasing industrial hygiene and safety without the buy-in of the workers running operations. One of the simplest yet most effective methods of bringing up safety scores is to simply slow down. While this mindset goes against the obsession with productivity and metrics typical of many facilities, it’s a rebalancing of modern reality with human ability.
Consider an experiment on seminary students asked to give a speech on “The Good Samaritan” parable. Researchers told one group their participants were already waiting, creating a hurry. The second group was told they had just enough time, and the third was told they had more than enough. Even given the topic of the speech, only 10% of the hurried participants stopped to render aid to someone in need as they crossed campus, while 63% of the unhurried students paused.
Technology has increased overall productivity but has also added responsibilities for workers without a corresponding drop in working hours or adequate time to absorb new information and procedures. Exhaustion and burnout can lead to mistakes that cause injuries and cost lives.
Recent legislation to shorten the average workweek, if passed, could reduce the burnout many feel, improving workplace safety. In the meantime, site leaders can emphasize quality over quantity and stress safety over metrics in determining raises and bonuses to decrease the temptation to cut corners to make numbers.
Improving Industrial Hygiene and Safety
Workplace injuries cost countless lives and disrupt operations. Improving industrial hygiene and safety demonstrates a commitment to a strong, healthy and thriving workforce.
Site owners and supervisors should periodically review the latest updates to improve their operations. Keeping workers safe decreases liability, enhances workflow and results in a happier, more productive environment.
* This article is written by Jack Shaw. Jack is a seasoned automotive industry writer with over six years of experience. As the senior writer for Modded, he combines his passion for vehicles, manufacturing and technology with his expertise to deliver engaging content that resonates with enthusiasts worldwide.
Industrial and collaborative robots have had a tremendous impact on the automotive industry, changing the standards for production, quality control and safety. In assembly, they have permanently shifted how workers and plant managers interact with machinery.
The State of Robots and Cobots in the Automotive Sector
Industrial and collaborative robots are foundational to the automotive sector. While they can seem similar at first glance, the two have fundamental differences. Their specialized designs and applications give them each a unique place in the industry.
Of course, industrial robots came first and have become the standard. They brought tremendous value to operations, leading to the automotive industry becoming one of the most mechanized industries. These heavy-duty machines outperform their human counterparts in tasks like material handling and part insertion.
Collaborative robots — often referred to as cobots — are meant to act as support rather than replacements. Their place on the factory floor is directly next to workers since they’re much safer than their industrial counterparts. They excel at precision-based tasks like bin picking, screw-driving and product dispensing.
Although traditional industrial robots have long been the industry standard, cobots have quickly grown in popularity. In the automotive sector alone, their combined global sales value was roughly 3.8 billion in 2022. Both technologies have significantly impacted worker safety, assembly efficiency and production yields.
The Rise of Robots and Cobots
In the automotive sector, the popularity of robotics is plain to see. Industrial robot installation increased by 31% between 2020 and 2021 alone, demonstrating how it has room to expand despite already being an industry staple. What makes this technology so highly sought-after?
Industrial robots have existed for ages and they are reliable. They are what’s known as mature technology, meaning their user base has eliminated most of their faults over the years. This consistency is crucial in the automotive sector, given the complex nature of the assembly line.
Cobots have quickly reached the popularity of industrial robots because they can adapt rapidly and outperform their counterpart regarding safety. Instead of being trapped in cages far away from humans, they work alongside employees on the factory floor. They open up many new opportunities for broadened automation and efficiency improvements.
Although most robot and cobot applications involve automation, worker safety and production capacity improvements have also proven significant. Humans no longer have to lift obscenely heavy objects or work in intense heat because their role requires it. Instead, the machines take over the dirty, complex and challenging tasks.
The Role of Robotics in Automotive Assembly
Robots and cobots have made a substantial impact on automotive assembly. Many factory floors now have humans and machinery working alongside each other instead of separately. Because of this development, plant managers have been able to automate duties they never previously could’ve.
Typically, monotonous manual work takes up most of the workweek. Across various industries, more than 40% of employees spend the majority of their workday on repetitive duties. Although the widespread adoption of industrial robotics has made the automotive sector somewhat of an outlier in this sense, there are still plenty of jobs left to partially or fully automate.
Even if demand changes, manufacturers can use cobots to continue automating whatever they need to. Since these machines are reprogrammable, their duties can adjust depending on a plant’s needs. For example, they could easily switch from bin picking to sealant dispensing to make up for an unexpected job vacancy or a sudden shift in consumer expectations.
Robots also protect the automotive industry from common pain points like labor shortages, human error and assembly line bottlenecks. This development is clearly visible with cobots, considering plant managers can support any manual duty with them and reprogram them at will.
These machines can safeguard production rates even in unforeseen circumstances. The COVID-19 pandemic impacted the sector significantly, causing unprecedented downtime. More than 50% of automotive companies experienced substantial disruption during this period. If facilities had a combination of robots and cobots, they likely could’ve avoided the effects of the sudden labor shortage.
The Impact of Robotics in Automotive Assembly
With robots and cobots, plant managers can fully or partially automate virtually any position in the assembly line. As a result, they can pursue highly-trained employees with more specialized skills. This development might eventually give rise to product quality improvements.
Robotics has also made labor condition improvements possible. In the past, workers had to do every hazardous or strenuous task by hand. Even with the introduction of industrial robots, they still risked injury and exhaustion. The development of cobots allowed them to work alongside each other.
Most importantly, robotics has vastly improved product yields. While Industrial robots are an industry staple, their large size, operational skill requirements and ability to injure workers hold them back. Cobots closed the gap, allowing plant managers to automate what was left.
Robotics Innovate Automotive Assembly
While cobots have quickly risen in popularity, traditional industrial robots are still vital parts of automotive assembly because they excel in heavy-duty tasks. A combination of both helps maximize efficiency, worker safety and product yields.
*This article is written by Jack Shaw. Jack is a seasoned automotive industry writer with over six years of experience. As the senior writer for Modded, he combines his passion for vehicles, manufacturing and technology with his expertise to deliver engaging content that resonates with enthusiasts worldwide.
The material handling industry is the backbone of globalized supply chains. However, it encounters a range of challenges, both internal and external. One notable external challenge is the impact of labor shortages on transportation and logistics, which are vital components of material handling operations.
To overcome these challenges, companies are making significant investments in technology. According to the 2023 MHI Annual Industry Report, 74% of supply chain leaders are increasing technology spending.
While capitalizing on advanced supply chain technologies can offer some respite, leaders may need to take more profound measures to effectively address the emerging issues.
In light of the survey responses featured in the MHI report, this article aims to explore the three primary challenges faced by the material handling industry.
#1: Worker safety
According to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics, there were 5,190 fatal work injuries in 2021, with 798 attributed to exposure to harmful materials or the environment — the highest figure since the series began in 2011!
Material handling operations often involve risky conditions for workers. From handling hazardous chemicals in facilities to lifting heavy loads in warehouses, workers in this supply chain sector regularly risk their health and lives.
Common causes of worker injuries in material handling include:
- improperly stored materials falling
- damaged storage units
- heavy manual lifting, pushing, or carrying
- exceeding loading limits on lifting equipment
- collision with materials or equipment.
Ensuring workers’ safety and security is vital and requires a multi-pronged approach. Safety negligence or violation can quickly become a compliance issue, resulting in monetary and reputational damage.
Material handling and supply chain companies address workplace safety challenges by providing personal protective equipment (PPE), delivering safety training, conducting equipment training, and performing safety audits.
Conscious companies that rely on manual labor also address the ergonomics of material handling in their safety training. Identifying ergonomic risk factors in manual or machine-supported lifting, carrying, and pushing jobs is critical for preventing fatigue and injury.
To prioritize the health and safety of their employees, conscious companies cultivate a “safety-first” culture. A prime example of a logistics company that excels in worker safety is DHL, based in Germany.
Safety is a core value for DHL, and they have implemented a holistic approach to address safety concerns through continuous training, strict compliance with regulations, and active employee engagement.
#2: Material and equipment damages
Poorly maintained equipment, untrained workers, and natural disasters can lead to expensive damages. Among these challenges, equipment damage stands out as one of the primary concerns for material handling companies, often resulting in downtime. In fact, unplanned downtime costs manufacturers a staggering $50 billion annually.
To ensure reliability and resilience, timely maintenance is crucial for all aspects of material handling operations, ranging from trucks and forklifts to pallets and sliding racks.
Similarly, it is equally important to prevent damage to the materials being handled by the equipment or workers. Well-organized warehouse loading and unloading processes, supported by well-trained workers and advanced technology, can effectively minimize material handling damages.
Many supply chain companies are leaning towards predictive maintenance solutions for equipment to ensure they are well-maintained for operations. Predictive maintenance leverages technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to predict potential problems with equipment and fleet.
In addition, these companies are minimizing accidents that result in costly damages through increased visibility. Warehouse inventory management and organization technology, for example, helps maintain optimal inventory levels, prevents overstocking, and ensures efficient use of storage space.
Gradesens, a Swiss company specializing in predictive maintenance, is helping logistics companies with very-narrow aisle warehouses proactively maintain automated systems for loading and unloading. With accurate and timely maintenance, the warehouses prevent downtime because of equipment failure.
#3: Controlling emissions
Carbon emissions are a huge problem for major industries, and material handling is no exception. With environmental organizations ringing alarm bells on rising global temperatures, material handling and supply chain leaders are paying close attention to sustainability.
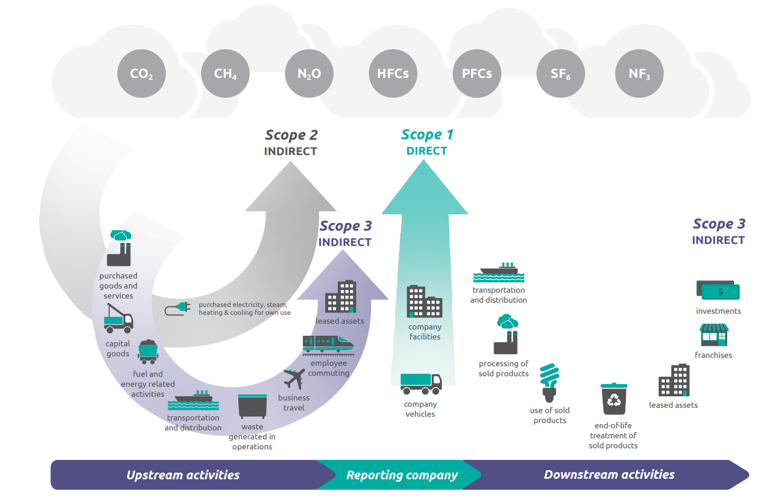
Material handling operations, including warehousing, contribute to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions through electricity usage, particularly natural gas. Additionally, using fossil fuel-powered vehicles and equipment contributes significantly to carbon emissions. Many material handling companies make up Scope 3 emissions for other organizations.
Fortunately, the material handling industry is adopting energy-efficient practices, thanks to environmental advocacy and pressure from governments with ambitious sustainability goals.
The MHI report revealed that organizations in material handling are investing in electrification, natural resource management, sustainable water consumption, and the transition to renewable energy.
Similarly, the European Logistics Supply Chain Sustainability Report found that 80% of surveyed companies consider sustainability a key focus area.
Material handling companies are reducing carbon footprint by investing in electric lift trucks. Electric forklifts have zero emissions compared to their counterparts powered by internal combustion engines.
Renewable energy has also been a focus for the industry, with major companies setting goals to go 100% carbon-neutral or net zero emissions. For instance, Amazon, the largest corporate buyer of renewable energy, uses clean energy in many fulfillment centers. The company plans to reach its 100% renewable energy goal by 2025.
The takeaway
Material handling is linked with virtually every industry, which makes its challenges essentially every industry’s challenges.
Some of the issues aren’t unique to material handling. For instance, sustainability is a global issue. The good news is that many companies are taking promising measures to combat these challenges: and technology is at the heart of these solutions.
It’s imperative for organizations in material handling to provide training and maintain equipment for better worker safety. Similarly, investing in clean energy solutions can go a long way in reducing emissions, which is good for the environment and business.

Matilda Odell
*This article is written by Matilda Odell. Matilda works as the Content Creation Specialist at the brand TAWI, a brand by Piab Group, which enables smart lifting optimized for people and businesses. Piab helps its customers to grow by transforming their businesses with increased automation. If you have any questions about lifting equipment such as vacuum lifters or other lifting devices, Matilda is the person to talk to.
Vaccine rollout is well underway in the U.S., painting a positive picture for the future. Still, it will take time for everyone to be fully vaccinated, and even then, COVID-19 safety protocols could linger for a while. In the meantime, workplaces can turn to automation to improve their anti-COVID-19 measures.
Temperature checks, social distancing, and mask mandates have become standard across many businesses. While necessary, enforcing these protocols can limit facilities’ productivity, as they rely on staff who could otherwise work on value-adding tasks. Since many companies had to reduce their active workforce by 39% on average, they need to improve productivity wherever possible.
Automating COVID-19 safety protocols also further removes employees from situations where they could contract the virus. Automation minimizes or eliminates close contact between workers during things like temperature checks.
Here’s how you can automate COVID-19 safety measures to stay safe and raise productivity.
1. Install Body Temperature Cameras
Temperature checks are one of the most common anti-COVID-19 measures, but they typically require close contact. Some businesses have found a way around this by installing thermal camera systems by employee entrances. These systems, which resemble metal detectors, scan worker temperatures as they walk, alerting relevant parties if they’re feverish.
Setting these systems up may be expensive at first, but you gain productivity in the process. The employee who would’ve performed temperature checks can instead work as usual, making your workplace more productive. Since these cameras can scan 30 people at once, they’re also more efficient than human-run checks.
Similar cameras throughout the workspace can detect if an employee develops a high temperature at work. You can then investigate further to determine if they need to go home or not.
2. Distribute Wearables for Social Distancing
Maintaining at least a 6-foot distance between workers is another crucial step in preventing COVID-19 outbreaks. Instituting a social distancing policy by itself isn’t enough to ensure people stay distant. It’s not economical to have managers monitor employees, either, so automation is the ideal solution.
Many warehouses and factories have turned to wearable technology to facilitate social distancing. These devices alert employees when they come within six feet of one another through noises and vibrations. These alerts are particularly helpful in areas with limited visibility where workers may not see each other.
You can’t expect to enforce social distancing by having managers roam the workspace. They can’t feasibly cover enough ground, and they could be working on more valuable tasks instead. Using wearables to maintain distance lets you keep employees safe without sacrificing productivity.

Photo by Torsten Dettlaff from Pexels
3. Use AI Cameras to Detect Masks
Masks are one of the simplest yet most effective ways to minimize the spread of COVID-19. Like with other regulations, though, mask mandates are only effective to the extent that employees comply with them. AI-enabled camera systems can detect if workers are wearing masks or not.
Machine vision systems can analyze video footage to see if anyone isn’t wearing a mask when they should be. You could deploy these with facial recognition to identify non-masked employees, but you may run into privacy concerns. An alternative would be a system that alerts managers when someone isn’t wearing a mask so they can look into it.
No matter what type of cameras you use, you should make sure your employees know about it. Privacy laws forbid employers from placing hidden cameras in private areas, and workers must know if and when you are recording them. Keep these factors in mind so you can protect employees from COVID-19 while preserving privacy rights.
4. Employ Sanitation Robots
Sanitation has found itself in the spotlight throughout the pandemic. Many businesses have adopted new cleanliness standards to eliminate cross-contamination and disease spreading through shared surfaces. Most companies pursue this by hiring cleaning crews or requiring workers to clean more frequently, which isn’t efficient.
A more cost-effective measure is to use sanitation robots. These automated cleaners are typically expensive but represent savings in the long run. Some take just 12 minutes to disinfect an area that would take a human worker more than an hour.
When you factor in how much it would take to pay a cleaning service over several months, the robots are more cost-efficient. Automation in this area also keeps people away from potentially contaminated surfaces, improving workplace health.
5. Implement Access Controls
Knowing where all employees are at any given time facilitates easier and more accurate contact tracing. Partitioning a workspace into separate zones can also help enable social distancing. To enforce these protocols more efficiently, you can use electronic access controls.
You can install locks that only open when workers scan their IDs. When employees have to scan into an area, you have a record of who was where if an outbreak occurs. You can then alert any other employees who might’ve contracted the virus so they can quarantine.
You could post workers by the doors to record who goes in and out, but that would be highly inefficient. Automatic access controls help ensure everyone working that day is adding value to the company.
Automation Improves Safety and Efficiency Amid COVID-19
Automating COVID-19 safety protocols lets you stay safe and maintain productivity. These solutions may come at a higher upfront cost, but their safety and efficiency benefits are impossible to ignore. They will also continue to help after the pandemic fades, ensuring productivity while preventing diseases like the flu.
COVID-19 has wreaked havoc on many businesses, but you can take measures to mitigate it. These five automation options will help keep your employees safe and efficient.
This article is written by Devin Partida. Devin is a tech writer with an interest in the IIot and manufacturing. She is also the Editor-in-Chief of ReHack.com.
The industrial and manufacturing sector is most affected by workplace accidents. Statistics show that at least 100,000 workers in the manufacturing industry are victims of job-related injuries every year. That’s why a company needs to have a culture that promotes safety. Here are a few tips that can help increase the safety of everyone in the company:
1. Always report any unsafe conditions.
As an employee, you get to interact with the equipment in the facility regularly. Therefore, you can know when something can lead to an accident. In such a case, report the matter to the supervisor. Supervisors are obligated to provide employees with a safe working environment, so they will take action to address the problem.
For example, a wet floor may not seem like a big deal on paper, but it can lead to slips and falls. Report the problem no matter how small it looks to make the working environment safe for everyone. As a supervisor, encourage your employees to report these unsafe conditions instead of terming them as small or frivolous.
2. Ensure Proper Usage of Equipment
Most industrial work-related injuries are a result of misuse of the tools and machines. As an employee, you should always use a machine for its intended purpose and nothing else. Most manufacturers provide instructions for usage. Use the instructions to operate the machinery.
Furthermore, always keep the working tools clean and inspect them before using. For example, a loose bolt on a wheel of a lorry may be a recipe for disaster. Checking the truck before leaving will ensure you notice the problem and fix it.
3. Always Wear Protective Gear
In a manufacturing firm, it is only logical to always have your PPEs on while working. Wear a helmet, gumboots, and mask if need be. As an employer, ensure that no employee in the company operates without wearing their protective gear. Don’t forget to inspect your equipment before every shift to ensure they are okay for maximum protection.
4. Don’t Overwork Your Employees.
Every industrial and manufacturing firm uses electrical tools. These tools require alertness, and a few mistakes can lead to fatal injuries. When someone is too tired, they are prone to making mistakes, and these mistakes can lead to serious work-related injuries.
For that reason, ensure that your workers take breaks throughout the day to maintain alertness. A brief break can ensure your employees return to their job alert and refreshed to complete the day.
5. Keep the working space organized and exits clear
When you keep the working space organized and clear, the probability of work-related injuries reduces drastically. A disorganized working area will limit the space you should use to lift heavy objects the right way. Additionally, keeping the exits clear will make sure you have somewhere to escape to in case of an emergency.
For David Rowland, Head of Marketing at Engage EHS, any business person worth their salt will have an in-depth knowledge of health and safety policy and practice. This is because health and safety is not only an end in itself, it is a means to an end towards a more efficient business that has an improved bottom line and greater brand loyalty amongst consumers.
Remember, safety starts with you. Therefore, be sure to keep these tips in mind while working in an industrial or manufacturing environment.
—
This article was written by Holly Shaw. Holly is a freelance industrial writer who focuses on quality industrial equipment and modern manufacturing. Holly is currently writing for SummitMT.
We’re all aware of the fact that COVID-19 has changed life as we know it in this country (and the world). Because of this pandemic, there is a new level of complexity in everything we do. Whether it’s having to mask up, sanitize grocery cart handles, and remember not to touch your face before washing your hands just to shop for your family’s dinner, or running your business’s operations safely by instituting new protocols designed to keep your workers healthy, COVID has inserted all sorts of new steps into old processes.
These are necessary evils, at least for now. But no matter if you’re talking about a grocery run or a manufacturing run, all of these new steps, protocols and procedures mean a drop in efficiency. Things just take longer now. For individuals going about their everyday lives, it’s a simple annoyance. But for businesses, it can mean a drain on the bottom line.
Efficiency busters in business
If you’re experiencing a drop in efficiency because of COVID protocols, you’re not alone. Most every business has instituted new procedures designed to keep their people safe and healthy. The unfortunate downside is, they can erode your efficiency. Here are some common efficiency busters brought on by the pandemic.
Temperature checks. Just getting on and off the shop floor now may involve temperature checks and other time-consuming safety protocols. When you’re measuring efficiency in minutes, this time lag when changing shifts can become problematic in a hurry.

Physical distancing. The COVID distancing guidelines (six feet, per the Centers for Disease Control) have caused manufacturing businesses to alter the configuration of their operations in order to accommodate the need for separation between workers. But that can mean fewer hands on the job.
Employee exposure. If one person on a shift is diagnosed with COVID, everyone who came into close contact with that person should isolate until they are tested or don’t develop symptoms within 14 days, according to CDC guidelines. Losing even a few team members for that amount of time is devastating.
Sanitization. Many businesses need to clean and sanitize workspaces, machinery and other tools of the trade between shifts, now more than ever before.
Supply chain slowdowns. COVID protocols worldwide may result in challenges getting people and materials to your business. Your supply chain may be affected by these same issues, causing a slowdown in getting the raw materials you need to and from your business. According to the Institute for Supply Management, purchasing managers at some of the largest manufacturing companies expressed ongoing unease about future shocks to their supply chain while they scramble to remedy current shortages.
[For more information about supply chain management, read our blog, 4 Best Ways Manufacturers Can Perfect Their Supply Chain]
Everyone’s productivity can be taken down a notch by these new protocols, procedures and delays.
How USCCG can help
By analyzing and implementing new strategies with getting your people on and off the shop floor faster, developing optimized layout plans to allow physical distancing, or improving processes for sanitization or what to do when employees develop symptoms, USC can assist. Most importantly, we can help you find hidden opportunities for efficiency that might mitigate some of that productivity loss. It’s crucial to look at your operations now. Operating like that proverbial well-oiled machine will be the key to you not simply surviving this crisis, but thriving now and in the future.
At USC Consulting Group, we have spent more than 50 years doing just that. We specialize in finding hidden opportunities for increasing process efficiency, allowing you to do more with the assets you already have. It’s about looking at your operations and finding efficiencies you’re not aware of.
If you’re interested in finding out more about how USC Consulting Group works, and what we can do for your business, please get in touch. That call today could lead to a more efficient operation tomorrow.
For more information about our current solutions to today’s operational challenges, read our free eBook, “Times Have Changed. USC Consulting Group Can Help You Adapt.”