-
Subscribe to Blog:
SEARCH THE BLOG
CATEGORIES
- Aerospace
- Asset Maintenance
- Automotive
- Blog
- Building Products
- Case Studies
- Chemical Processing
- Consulting
- Food & Beverage
- Forestry Products
- Hospitals & Healthcare
- Knowledge Transfer
- Lean Manufacturing
- Life Sciences
- Logistics
- Manufacturing
- Material Utilization
- Metals
- Mining
- News
- Office Politics
- Oil & Gas
- Plastics
- Private Equity
- Process Improvement
- Project Management
- Spend Management
- Supply Chain
- Uncategorized
- Utilities
- Whitepapers
BLOG ARCHIVES
- July 2025 (1)
- June 2025 (4)
- May 2025 (1)
- April 2025 (1)
- March 2025 (1)
- February 2025 (4)
- January 2025 (4)
- December 2024 (4)
- November 2024 (2)
- October 2024 (6)
- September 2024 (5)
- August 2024 (5)
- July 2024 (6)
- June 2024 (3)
- May 2024 (3)
- April 2024 (4)
- March 2024 (3)
- February 2024 (4)
- January 2024 (5)
- December 2023 (2)
- November 2023 (1)
- October 2023 (6)
- September 2023 (3)
- August 2023 (4)
- July 2023 (2)
- June 2023 (3)
- May 2023 (7)
- April 2023 (3)
- March 2023 (3)
- February 2023 (5)
- January 2023 (6)
- December 2022 (2)
- November 2022 (5)
- October 2022 (5)
- September 2022 (5)
- August 2022 (6)
- July 2022 (3)
- June 2022 (4)
- May 2022 (5)
- April 2022 (3)
- March 2022 (5)
- February 2022 (4)
- January 2022 (7)
- December 2021 (3)
- November 2021 (5)
- October 2021 (3)
- September 2021 (2)
- August 2021 (6)
- July 2021 (2)
- June 2021 (10)
- May 2021 (4)
- April 2021 (5)
- March 2021 (5)
- February 2021 (3)
- January 2021 (4)
- December 2020 (3)
- November 2020 (3)
- October 2020 (3)
- September 2020 (3)
- August 2020 (4)
- July 2020 (3)
- June 2020 (5)
- May 2020 (3)
- April 2020 (3)
- March 2020 (4)
- February 2020 (4)
- January 2020 (4)
- December 2019 (3)
- November 2019 (2)
- October 2019 (4)
- September 2019 (2)
- August 2019 (4)
- July 2019 (3)
- June 2019 (4)
- May 2019 (2)
- April 2019 (4)
- March 2019 (4)
- February 2019 (5)
- January 2019 (5)
- December 2018 (2)
- November 2018 (2)
- October 2018 (5)
- September 2018 (4)
- August 2018 (3)
- July 2018 (2)
- June 2018 (4)
- May 2018 (3)
- April 2018 (3)
- March 2018 (2)
- February 2018 (2)
- January 2018 (1)
- December 2017 (1)
- November 2017 (2)
- October 2017 (2)
- September 2017 (1)
- August 2017 (2)
- July 2017 (2)
- June 2017 (1)
- April 2017 (3)
- March 2017 (3)
- February 2017 (2)
- January 2017 (2)
- December 2016 (2)
- November 2016 (4)
- October 2016 (4)
- September 2016 (3)
- August 2016 (6)
- July 2016 (4)
- June 2016 (4)
- May 2016 (1)
- April 2016 (3)
- March 2016 (4)
- February 2016 (2)
- January 2016 (4)
- December 2015 (3)
- November 2015 (3)
- October 2015 (1)
- September 2015 (1)
- August 2015 (4)
- July 2015 (6)
- June 2015 (4)
- May 2015 (7)
- April 2015 (6)
- March 2015 (6)
- February 2015 (4)
- January 2015 (3)
CONNECT WITH US
Tag Archives: Supply Chain
Operational excellence is the pursuit of enhanced efficiency and effectiveness in business processes. Traditionally, companies relied on established methods to optimize their operations. However, artificial intelligence (AI) and data science now augment traditional practices, leading to innovations in Lean manufacturing.
Lean manufacturing remains foundational to operational excellence. Its principles — such as continuous improvement, process optimization, and employee engagement — help organizations adapt to changing market demands. For instance, companies that implement Lean practices can respond swiftly to customer needs, reduce lead times, and improve product quality.
Sticking to lean principles is crucial; they not only enhance flexibility and engagement among employees but also position companies better to manage supply chain disruptions and fluctuations in demand. By embracing these methodologies, businesses can achieve long-term growth and get ahead of the competition.
AI and Automation in Operational Excellence
AI-driven automation is revolutionizing business operations by improving efficiency and innovation. By integrating intelligent algorithms, organizations can streamline processes and reduce manual intervention, enabling employees to focus on higher-value tasks. For instance, predictive analytics allows companies to anticipate customer needs and align production schedules accordingly, minimizing waste and maximizing output — core tenets of Lean manufacturing.
Strategic AI approaches, such as machine learning for demand forecasting, empower businesses to adapt swiftly to market fluctuations. Companies like Amazon use AI to optimize inventory management, ensuring products are available when needed while reducing excess stock. Similarly, AI-powered chatbots improve customer service by providing instant support, increasing engagement and convenience.
Moreover, automating routine tasks both accelerates operations and fosters a culture of ongoing improvement. As employees embrace AI tools, they are encouraged to find opportunities for innovation. Ultimately, these AI-driven strategies position organizations to thrive in a competitive landscape, exemplifying the synergy between technology and Lean principles.
Leveraging Data Science to Identify Inefficiencies
Data science plays an instrumental role in analyzing and improving business operations by using vast amounts of data to uncover patterns, trends, and insights. By employing statistical methods and algorithms, businesses can identify inefficiencies within their processes, leading to data-driven decision-making.
The synergy between data science and AI amplifies this effect. AI algorithms can quickly analyze complex datasets, enabling predictive analytics that foresee customer behavior and operational challenges. For example, machine learning models can optimize supply chains by predicting demand fluctuations, which helps reduce costs and improve service delivery.
Together, these technologies encourage a proactive approach to performance optimization. Businesses can continually refine their operations, respond agilely to market changes, and ultimately maximize customer satisfaction. Therefore, integrating data science with AI not only helps in identifying inefficiencies but also drives growth and competitive advantages.
Integrating Lean Practices with AI and Data Science
Lean practices focus on eliminating waste and improving efficiency, while technology-driven strategies leverage AI and data science to enhance operations. The integration of these methodologies allows companies to create a robust operational framework that is both agile and efficient.
Organizations can employ AI for real-time data analysis to support Lean initiatives. This enables quicker identification of process bottlenecks and focal areas for improvement. When combined with data science, businesses can employ predictive analytics to anticipate customer demands accurately, facilitating proactive decision-making.
Companies like Coca-Cola and Unilever have successfully harnessed advanced technologies such as AI and data analytics to streamline operations. Coca-Cola utilizes AI to optimize its supply chain and enhance customer engagement, while Unilever employs machine learning for demand forecasting, allowing for better inventory management. Both organizations demonstrate how integrating advanced technologies can lead to improved efficiency and responsiveness in a dynamic market.
Real-World Applications: Reducing Waste and Streamlining Processes
To enhance supply chain efficiency, organizations can leverage AI, data science, and Lean methods to identify and eliminate key sources of waste. For instance, AI-driven analytics can uncover overproduction by predicting demand more accurately, allowing companies to align their manufacturing with customer needs. Data science can optimize inventory levels, reducing excess stock and storage costs by implementing just-in-time inventory systems.
Additionally, Lean principles advocate for minimizing motion waste by redesigning workplace layouts and streamlining processes. Using motion studies can identify unnecessary movements in warehouses, enabling the creation of more efficient workflows.
By addressing common sources of supply chain waste, such as waiting time, overprocessing, and poor route planning, organizations can create a waste-resistant distribution chain. Route optimization software improves transportation efficiency, reducing fuel costs and delivery delays. Collectively, these strategies not only cut costs but also enhance customer satisfaction and employee morale, fostering a more effective and responsive supply chain.
Conclusion
The evolution of operational excellence has increasingly integrated AI, data science, and Lean practices, creating a framework for sustainable growth and competitive advantage. This enables organizations to use real-time data analytics, enhancing decision-making and facilitating agility in operations. AI can predict customer demand more accurately, minimizing overproduction and optimizing inventory levels, while Lean principles focus on eliminating waste and streamlining processes.
The benefits of this integration are profound: reduced costs, improved efficiency, and maximal customer satisfaction. By harnessing advanced technologies, companies can identify process bottlenecks and enhance supply chain efficiency, positioning themselves adeptly in a dynamic market environment.
Looking ahead, the future of operational excellence will see deeper integration of emerging technologies, fostering a culture of continuous improvement. Organizations that embrace this will improve their operational capabilities and innovation, ensuring they remain competitive in an increasingly complex business landscape.
*This article is written by Ainsley Lawrence. View more of Ainsley’s articles here.
When managing your supply chain, it’s crucial to be aware of the latest technologies and how to integrate them with your existing systems. Doing so will optimize the efficiency of your operations and boost transparency. To benefit from updated technology, you may first encounter some obstacles during implementation.
This article explores common barriers to adopting technology and provides strategic insights into overcoming these obstacles so your organization can maximize the benefits of technology advancements.
Common Barriers to Tech Adoption and How to Overcome Them
As you participate in the global supply chain systems, you may encounter a variety of common barriers to adopting technology effectively. Common barriers include:
Integration complexities
If you’ve been in business for a significant amount of time, your team will likely have legacy systems that are challenging to integrate with emerging technologies. It’s best to integrate new technologies slowly and methodically.
Prudent managers will create change management strategies to ensure the process goes more smoothly. Companies can work with supply chain integration services, which cover strategic decision-making and setting up integration teams when working with new technology solutions.
Budgetary limitations
One common objection in management to deploying modern technology is the expense of investment and maintenance. But you have to spend money to make money and avoid the opportunity cost that would result from failing to adopt a promising technology.
A strategic move would be to demonstrate the return on investment in Software as a Service, or SaaS, and how adopting new technologies will provide you with significant long-term savings.
For example, you can calculate how much money your organization could save if you migrated data and software services to a cloud computing solution, which would have a dedicated staff of IT experts keeping watch over your information. This will be less expensive than maintaining your own data servers and trying to predict how much capacity you’ll require.
Cloud computing lets your supply chain stakeholders connect to data from any location safely and securely, fostering greater collaboration using mobile devices when they’re not near a desktop computer.
Data security concerns
As you adopt new technology, you must understand the security implications of its use. Criminal hackers may try to invade the privacy of employees who maintain your supply chain.
They may attempt to breach your network with malware — which can lead to theft of intellectual property or lock down data during a ransomware attack — and threaten to not restore access to crucial information until you pay the ransom. You’ll want to implement advanced protocols to ensure optimized cybersecurity. It’s prudent to make sure you comply with global data privacy restrictions.
Workforce training needs
You may have been facing a shortage of skilled workers who can help you deploy and manage new supply chain technologies. Accordingly, you’ll need to invest in development and training.
Often, it’s best to partner with external consultants, whether you’re improving your onboarding process or overhauling the ongoing training you provide to long-standing members of your team.
You want to engage your employees so they can work to their maximum potential within the supply chain. For example, give them wearable mixed reality devices to provide them with additional content to enhance how they carry out complex tasks and work more safely.
Without the Latest Technology for Supply Chain Integration, You May Fall Behind the Competition
Owners and managers of businesses with significant reliance on the global supply chain cannot keep their heads in the sand regarding technology. It pays to hire supply chain experts with a background in technology to pave the way toward optimized integration.
Companies without in-house expertise can partner with firms that specialize in supply chain integration services. Doing so will help you maintain a competitive edge and work more efficiently and transparently.
*This article is written by Gary Brooks. Gary is the CMO of ketteQ and has more than 25 years of experience leading marketing for top software companies. Brooks has been featured in major publications such as Forbes, VentureBeat, ZDNET, Equipment World, Nikkei, Manufacturing Business Technology, Supply & Demand Chain Executive, and Field Service News, among others. Brooks holds a BS from Northeastern University and an MS, Management from Lesley University. He also is the co-founder of the Brooks Family Foundation.
Labor shortages, supply chain disruption, and technological change have been cause for concern for executives in the manufacturing industry the last few years. As 2024 draws to a close, business leaders are looking ahead to the coming year. What will manufacturing be facing in 2025?
Here are five trends and challenges we’re expecting for the manufacturing industry in 2025 and advice on how to handle each issue.
1. Digital transformation
It’s not that AI and technology are coming for people’s jobs. It’s about this technology being able to streamline how the job gets done, adding speed, quality, and efficiency to the process. The 2024 Manufacturing and Distribution Pulse Survey Report by Citrin Cooperman found 43% of leaders in manufacturing are currently implementing advanced tech programs and policies in their organizations.
It’s involving AI and Machine Learning to optimize processes and outcomes, the Internet of Things (IoT) which will use smart technology to have machines communicate their own glitches and needs for maintenance, and robotics and automation for tasks like assembly.
The end goal is to increase predictive maintenance, optimize processes, ramp up quality control and provide real-time data for better decision making.
What manufacturing should do:
At USC, we help clients use AI, Machine Learning, and Predictive Analytics to optimize their workflows, processes and demand forecasting. Companies should be using these techniques now, if they’re not already. It’s also crucial to upskill existing employees to be able to work with the new technologies. That’s a win-win for manufacturing companies and their workforce. Higher skilled employees are happier, more effective, and more loyal to the company.
2. Talent
Workforce development, skills gaps and employee retention will be the top issues in regard to talent in 2025. It has been estimated that 1.9 million manufacturing jobs could go unfilled over the next decade if talent challenges aren’t solved. The old guard, long term, experienced employees that executives rely on to get the job done are retiring without a strong pipeline of younger workers to take their place. In addition, the labor force itself is concerned with flexibility, hours, pay, child care and more.
But there’s also the issue of skills. A new study by Deloitte and the Manufacturing Institute found that the need for roles requiring higher-level skills, including technical, digital and soft skills are growing at a rapid rate.
What manufacturing should do:
Working with local trade schools, community colleges and even high schools to offer internships and apprenticeships is a great way to build the talent pipeline.
Also, offering current employees training in digital skills, as well as soft skills like leadership and management training, will provide the company with higher-skilled workforce. This will create a sense of loyalty and pride in the employee knowing the company is investing in them with an eye toward the future.
3. Sustainability
The focus on sustainability is everywhere. Manufacturers are feeling increased pressure to become greener, and as a result are implementing environmental, social and governance strategies.
There is governmental pressure because of tighter environmental standards, but there is also pressure coming from consumers who increasingly want and seek out goods that are manufactured with “clean” methods.
What manufacturing should do:
Continuing to investigate efficient technologies like solar and wind, and making investments in machinery and other assets that are more energy efficient, will be crucial in the coming year and beyond. It will help lower operating costs while satisfying the demand from consumers.
4. Supply chain
Supply chain disruption that plagued just about every business on the planet during the pandemic has eased to a great extent, but challenges are still out there. Lead times for materials is still high, and the cost of transportation and logistics is weighing on companies’ bottom lines.
Shipping delays and uncertainties are a big part of the problem, with headlines nearly every day of yet another cargo ship being attacked at sea.
Then there’s the issue of labor shortages all along the supply chain, both in foreign countries and the U.S., with labor strikes slowing down delivery and labor shortages of truck drivers adding to the snarl.
What manufacturing should do:
It’s extremely challenging for companies to combat labor shortages and shipping delays in their supply chains, but smart demand forecasting and considerations like reshoring supply sources can help. In addition, establishing a strong Sales, Inventory, and Operations Planning (SIOP) program will optimize your supply chain.
5. Tariffs
With a new administration may come new global trade policies, and it’s not just the U.S. that held elections in 2024. Many countries around the globe are restructuring leadership. Ongoing U.S.-China trade tensions will certainly intensify as a result of the tariffs the new administration is proposing, driving up the cost of materials for manufacturers.
What manufacturing should do:
Many manufacturers are ordering supplies and materials now, before the new administration takes over. Stocking up now, in case of major price hikes later.
This issue goes hand in hand with supply chain disruption and is one more reason to consider reshoring and nearshoring of supplies and materials.
The Outlook
Despite ongoing challenges, 2025 looks bright for manufacturers to grow their businesses. Adapting operations to be sustainable and incorporating advanced technology with an upskilled workforce to manage it, business leaders will enjoy major improvements to productivity, their supply chain, and customer satisfaction.
At USC Consulting Group, we’re here to help manufacturing companies become more productive and profitable with standardized operating procedures, enhanced management operating systems, SIOP improvements, and other strategies to find opportunities for greater efficiencies, increased throughput and bottom line results. Contact us today to have your operations humming in 2025.
The nature of supply chains has evolved over the years, with new technologies and many players in the middle making logistics highly complicated and expensive. A report by PwC indicates that logistics and supply chain costs account for approximately 10% of the organization’s total expenses. This is the most costly issue businesses struggle to minimize in their supply chain operations.
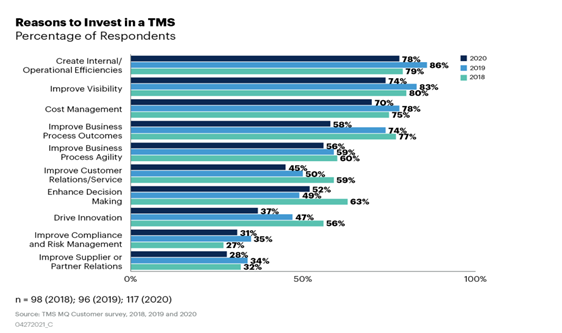
Managed transportation systems (MTS) address this problem, providing an organized way of consolidating logistics and eliminating waste. According to Gartner, the transportation management systems (TMS) market is expected to grow by 60%. This boom exemplifies the role of MTS in adapting to the prevailing dynamics of supply chain management.
This article will define MTS within the supply chain, reveal its operational and financial advantages, and explain how companies can embed them within their current structures and processes without disruption.
Benefits of Using Managed Transportation Systems
Managed transportation systems (MTS) go beyond optimizing shipping routing and data analysis management. They help manage logistics, allowing companies to concentrate on their primary business operations. Outsourcing the transportation management systems promotes professional development within the organization. It also enhances efficiency by eliminating wastefulness and saves costs in the long run.
The following are key benefits of using MTS in your supply chain processes:
Risk Management
Risk management has become more crucial now than ever because disruptions are bound to impact a company’s performance in its logistics industry. A managed transportation system can reduce risk by controlling carrier relationships and fine-tuning supply chain networks while using data-driven predictive tools to prevent delays or inefficiencies.
Cost Savings
Managed transportation systems assist organizations in selecting appropriate carriers and routes. This helps marketers cut transportation costs. In fact, companies that use data-driven insights can make well-organized decisions geared toward saving and managing costs effectively in the long run.
Simplified Day-to-Day Operations
If your company outsources logistics management, it can concentrate on its core business activities, such as developing new products and servicing customers. MTS providers manage logistics complexities, from booking shipments to addressing issues that may arise, so internal resources can be focused on core operations, increasing operational efficiency.
Enhanced Data and Insights
MTS analytics helps businesses monitor where logistics failed in real time. These insights allow businesses to make timely decisions, reduce delivery time, and optimize supply chain operations. Research indicates that data analytics helps cut costs and improve service levels.
Achieving Cost Efficiency with Managed Transportation Solutions
To stay competitive in the logistics market, your business must focus on reducing the cost of operations. But how do we achieve this? It’s pretty simple: Integrate managed transportation systems into your business.
Here are some vital hands-on ways to guarantee cost-effectiveness with MTS.
Carrier Optimization
Cost efficiency starts with choosing the appropriate carrier. MTS providers are not always out to settle on the cheapest rates but instead aim to optimize carrier selection by balancing cost and service performance. This guarantees timely deliveries and reduces transport costs.
Route and Mode Optimization
MTS helps companies find an optimum route and transport mode, resulting in huge cost savings. Increased route planning and mode selection for faster transit times help save on fuel consumption.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Data analytics are essential tools in minimizing a company’s costs. MTS vendors gather information from multiple systems and provide organizations with intelligence regarding logistics activities. Predictive and prescriptive analytics help forecast demand, anticipate disruptions, and make informed decisions that drive long-term cost savings.
Harnessing Data-Driven Insights for Superior Supply Chain Management
As supply chains grow more complex, data and analytics have become more than an optional add-on; they have become enablers of efficiency and resiliency. With the situation becoming even more complicated due to global disruptions, regulatory demands, and changing market conditions, data-driven approaches can bring a paradigm shift in supply chain management.
Here’s how businesses can capitalize on data-driven capabilities to improve the efficiency of their supply chain.
Supply Chain Data Management
Effective data management is the backbone of survival in the modern supply chain. There is an increasing reliance on advanced analytic tools for managing large volumes of data, which warrants quick insights and quicker actions.
According to KPMG’s Future of Supply Chain report, 39% of global supply chain professionals say they will invest in digital technologies to strengthen their data analysis capabilities. The readily available data enables an organization to anticipate interruptions, enhance visibility, and support efficient actions that maximize costs and service.
AI-Enabled Supply Chain Planning
Traditionally, demand planning is frequently carried out across departments using antiquated methods. This always leads to slow and less accurate forecasts. Fortunately, using AI-powered supply chain planning, the gaps between internal and external data can now be eliminated by leveraging unique machine learning models that link disparate types of information into a much more accurate forecast.
Generative AI in Supply Chain
Generative AI (GenAI) can transform supply chain management by making automation and decision-making easy. Examples of Gen AI use cases are translating complex data, summarizing legal documents, and analyzing customer feedback in real time.
Gen AI helps supply chain leaders more easily spot early warning signs, such as disruptions in supplier countries. It also supports faster response due to its capacity for handling huge amounts of information.
Best Practices for Leveraging Managed Transportation Systems in Your Business
A managed transportation system is a significant step and must be planned accordingly. Some best practices can help guide the process and ensure business gain from these systems.
1. Evaluate the Specific Needs of Your Business
Each company has different logistics requirements, and there may not always be a one-size-fits-all answer. When choosing a managed transportation provider or system, map your specific needs and see if they align with what they have—this is key. Shipment volume, frequency, and where you operate your business are some things to reflect on.
2. Monitor Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Measuring success for managed transportation system metrics begins with setting KPIs as they provide the capability to formulate results and track ongoing progress. Some metrics to monitor in your LSP are on-time delivery rates, transportation cost per shipment, and how fuel-efficient they run. Frequent monitoring of these KPIs will help determine the probable areas where the system could be improved to deliver desired outcomes.
3. Focus on Continuous Improvement
The logistics industry is ever-changing, and what works today may not work tomorrow. Businesses should be proactive agents, constantly assessing their managed transportation system and making informed course corrections based on data intelligence and performance metrics.
While this explanation can be more in-depth, businesses that embrace these best practices will have a smoother deployment of their managed transportation system and the operational as well as cost-saving results they expect.
Conclusion
There are many benefits of using managed transportation systems for businesses trying to improve supply chain efficiency and cost savings. MTS gives companies the tools needed to modernize logistics by delivering real-time visibility, route optimization, and data-driven decision support so that carriers can gain a competitive advantage in an increasingly complex supply chain. By deploying these systems, businesses can reduce costs and improve compliance and overall customer satisfaction.
*This article is written by Sheer Logistics. Sheer Logistics provides technology-driven supply chain solutions that empower businesses with visibility, efficiency, and agility across their logistics operations. With a focus on transparency and strategic partnership, Sheer Logistics helps clients optimize their supply chains and drive sustainable growth.
When cargo theft occurs, the entire supply chain suffers. Manufacturers must be aware of these recent trends occurring and act accordingly to protect their assets. With smart planning, businesses can adequately thwart thieves and safeguard their employees. Here are considerations for manufacturers to move in the right direction.
1. Understanding the Most Significant Risks
First, companies should understand the specific threats to which they are most vulnerable. The most immediate danger could be trucks in unsecured areas where thieves can quickly access them. In other instances, manufacturers may see organized crime targeting highly valued goods. Regardless, business owners need to acknowledge their weaknesses.
Researchers have investigated risk influential factors (RIFs) to determine the most damaging aspects. A 2022 study published in Reliability Engineering and System Safety developed a data-driven Bayesian network model to predict and diagnose cargo theft. The experts said product category, year, region, location type and modus operandi are the most significant RIFs. Therefore, manufacturers should be aware of these guidelines.
2. Leveraging Advanced Algorithms
Improving cargo security has become more challenging due to increased attack surfaces and opportunities for outside threats. In response, manufacturers must leverage advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to protect their assets. Algorithms are excellent tools for business owners because they reduce the theft risk when transporting goods on the road.
A 2024 study published in Computers and Industrial Engineering used a physical internet-based analytic model to combat rising cargo theft. The researchers used real-world scenarios in their experiments to understand the benefits and drawbacks. Their model determined the risk of different product types based on their specific routes, allowing them to better understand the threshold where shipments become vulnerable to criminal organizations.
3. Using the Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT devices are critical for management operating systems (MOS) because they enhance software and hardware capabilities. With these gadgets, manufacturers can improve productivity and financial performance. IoT research is also critical for securing cargo through each step of transit. For instance, GPS technology provides real-time knowledge of each shipment.
Manufacturers should take advantage of IoT because it can be present with the device and around the facility. Smart cameras are an excellent example because business owners can remotely monitor the feeds and promptly take action. Advanced technology also lets manufacturers take extra steps to protect their cargo. Smart locks with biometric recognition are a vital safeguard against thieves.
4. Improving Cybersecurity Practices
Cargo theft increased by 46% in the first quarter of 2024 compared to the same time in 2023. CargoNet reported 925 incidents in the quarter, emphasizing the need for heightened security tactics. While physical barriers are necessary, manufacturers should also improve their cybersecurity practices. Internet crime is equally damaging to companies and could be more challenging to predict.
Ransomware attacks are among the most pivotal for manufacturers, considering their frequency. A 2022 IBM report found that 23% of these incidents affected manufacturing, making it the most targeted industry. Preventing ransomware attacks entails basic to advanced cybersecurity tactics, such as multifactor authentication, anti-malware software and software updates.
5. Selective Supplier Partnerships
Some manufacturers outsource specific tasks to reduce overhead and strengthen their bottom line. In addition to these partners, companies must watch other links in the supply chain. Businesses should monitor supplier relationships to ensure security — otherwise, they risk lost revenue and downtime while fixing errors.
Supplier relationships start with background checks and regular audits. Manufacturers must ensure these partners do their best to detect and address vulnerabilities. Business owners should find companies with pertinent industry certifications like C-TPAT if applicable. Monitoring should continue throughout the relationship with consistent communication and key performance indicators (KPIs).
6. Properly Training Employees
While suppliers can be security liabilities, it’s equally essential for manufacturers to monitor their employees. Workers may willingly or unknowingly contribute to cargo theft through their actions, so businesses should protect them from themselves. First, company leadership should train employees on best security practices, such as reporting procedures and proper loading.
Then, the company should focus on internal theft from its workers. Experts say over 75% of employees have stolen from their employer at least once. Therefore, robust internal measures should be in place to prevent theft. Mitigating employee stealing includes restricting access control and using biometric scanners. Business owners could also encourage workers to be vigilant of suspicious activity.
7. Controlling Supply Chain Aspects
Ultimately, it’s up to manufacturers and business owners to control as many supply chain aspects as possible. Internal audits are a valuable tool because they reveal gaps in shipments and where theft has potentially occurred. Once a company understands its insufficiency, leadership teams can act accordingly. Businesses should audit their inventory, security and other critical business features.
Supply chain professionals should also regain control in areas they may consider less secure, such as transit. Highways and oceans provide plenty of unknowns, so businesses must protect their cargo before, during and after the route. Besides GPS devices, forward-thinking companies wield electronic seals, telematics devices, light sensors and other tech.
Tackling Theft and Protecting Assets
The rise in cargo theft should alarm manufacturing professionals and business owners. Outside threats have become more sophisticated through physical and cybersecurity risks. While crimes have increased, manufacturers should proactively combat thieves. Leadership teams should scrutinize suppliers, employees and other aspects of the supply chain to ensure safety.
*This article is written by Jack Shaw. Jack is a seasoned automotive industry writer with over six years of experience. As the senior writer for Modded, he combines his passion for vehicles, manufacturing and technology with his expertise to deliver engaging content that resonates with enthusiasts worldwide.
As technology continues to improve, large companies and supply chain manufacturers have more opportunities to expand their businesses and reach more customers with their products. With this power comes responsibility, calling for transparency in supply chains.
Reliable tracking systems must be implemented to enhance supply chain transparency and ensure businesses and customers get the accurate information they need. Real-time visibility platforms (RTVP), new technology and optimized data collection can create more visible supply chains.
What Is a Real-Time Visibility Platform?
Real-time visibility allows for the tracking and monitoring of products and goods, from pickup to delivery. With real-time data, all steps involved in the supply chain process are receivable, making it much easier for large companies to provide honest product and transportation details.
Real-time visibility platforms are the software tools and technologies that make this data possible. RTVP gathers data based on live updates on product location and status.
What Technologies Play a Part in Real-Time Visibility?
Like many things today, real-time visibility would not be possible without technology. As systems continue to grow, so does the potential for full transparency.
Many technologies work together to make real-time visibility possible. The following are some of the tools used to streamline processes and maximize supply chain transparency:
1. GPS
GPS technology has become an integral part of the real-time visibility process and enables RTVP to track objects for accurate data. GPS technology uses satellite signals and signal reception to capture the location of items, roads and buildings, and it sends this data back to our devices.
GPS technology does wonders for the transportation industry. By accurately tracking trucks and other transportation vehicles, we can watch products travel from point A to point B and make decisions based on their location.
2. AI
Artificial intelligence has entered many realms of society, including the supply chain. Fortunately, AI makes RTVP possible for various transparency purposes.
AI considers all factors and works alongside humans to enhance decision-making and efficiency, leading to a faster, safer and more honest supply chain. AI also powers advanced analytics to help humans and businesses analyze real-time data, making it applicable to all industries.
3. Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT creates a robust network that allows data to flow freely and improves connection and communication between different devices. Through this created network, IoT can narrow down specific items and points of data to share information and even make decisions.
From quantity to fulfillment, IoT processes data through algorithms that contribute to accurate, real-time visibility.
4. Blockchain
Blockchain acts as a safety tool for RTVP, “blocking” hackers and other forms of data manipulation. There are four main types of blockchain: public, private, hybrid and consortium. Each form creates a securely shared network of data that allows parties to communicate.
Blockchain allows equal access for all parties, and there is no single network owner. This provides for ethical, open movement throughout the supply chain and adds transparency to traditional supply chains.
Why Implement a Real-Time Visibility Platform?
Real-time visibility platforms provide endless benefits to supply chain industries. RTVP acts as a high-functioning network of technology and intelligence to help businesses identify areas for improvement and solve problems in all areas — from ethical to logistical.
With RTVP, there is no shortage of possibilities. The following are four benefits of implementing a real-time visibility platform:
1. Ensure Customer Satisfaction
Without RTVP’s technology, product location and safety are unknown to businesses and customers. When companies implement a real-time visibility platform, “the unknown” is eliminated. With access to knowledge such as when and where their goods will arrive, customers know exactly what to expect.
RTVP shares information with customers they previously did not have access to, such as ETAs and tracking details. The more customers know, the happier they will be!
2. Speed up Reaction Time
RTVP gives companies the power to detect precisely when and where disruptions occur, from departure to arrival. If an issue arises along the way, businesses know in real time, allowing them to immediately develop a direct course of action.
Companies can mitigate risks with transparent access to data, which reduces wasted time spent planning strategies and reacting to issues. RTVP allows for the tracking of delays, traffic, congestion, weather and anything else that could pose a potential threat.
3. Reduce Costs
Implementing a real-time visibility platform provides many financial benefits. Companies have access to trucks and products, allowing them to see available capacity and, in turn, utilize all available space. This creates sustainable, efficient transportation and also cuts costs.
Many industries are now dealing with labor shortages, rising material costs and an ever-changing risk landscape. With RTVP, industries can detect traffic, weather conditions and other risks to product transportation, reducing the risk of unnecessary financial burdens. With saved time and money, industries can focus on solving more significant issues.
4. Improve Relationships
RTVP uses technology to improve relationships between all parties involved. With transparency and proper information sharing, people can access honest details, avoiding the risk of being blindsided or misinformed.
Transparency positively impacts shippers, managers, workers, clients and customers, resulting in better collaboration and more satisfied people. RTVP also enhances communication, allows for honest lane sharing and improves handoffs and business interactions.
Use RTVP for Supply Chain Transparency
RTVP allows supply chain leaders and manufacturers to stay ahead of their industry and interact with advanced modern technology. Businesses can work hand in hand with real-time data to make their processes more efficient and keep customers satisfied. With RTVP, transparency is possible.
***This article is written by Jack Shaw. Jack is a seasoned automotive industry writer with over six years of experience. As the senior writer for Modded, he combines his passion for vehicles, manufacturing and technology with his expertise to deliver engaging content that resonates with enthusiasts worldwide.
Spend analysis is essential, yet complex and most organizations are unaware that spend analysis can be simplified and accelerated by implementing a structured system like the United Nations Standard Products and Services Code (UNSPSC).
In today’s competitive landscape, accurate and insightful spend analysis is critical for organizations to manage procurement efficiently, identify savings opportunities, and drive strategic purchasing decisions. However, many companies struggle with inconsistent data classification, making it challenging to gain meaningful insights. This is where UNSPSC classification can make a significant difference.
Understanding UNSPSC
The United Nations Standard Products and Services Code (UNSPSC) is a globally recognized system designed to classify goods and services. Its hierarchical structure includes segments, families, classes, and commodities, allowing for a granular approach to categorizing products and services across regions, suppliers, and industries.
By applying UNSPSC codes to procurement data, companies can standardize and streamline their spend analysis, enabling more efficient procurement processes and better decision-making.
The Impact of UNSPSC on Spend Analysis
Standardization of Data
One of the most significant challenges in spend analysis is dealing with inconsistent data across departments, suppliers, or geographic locations. Without a standardized classification system, companies often struggle to compare or consolidate spend data meaningfully. UNSPSC addresses this by providing a consistent framework that ensures all products and services are classified uniformly. Whether your business operates in multiple countries or deals with various suppliers, UNSPSC enables a cohesive and structured view of your procurement activities.
Improved Visibility into Spend Categories
The granularity provided by UNSPSC allows businesses to break down their spending into specific categories, such as office supplies, IT equipment, or professional services. This level of detail helps organizations pinpoint their most significant spending areas and uncover opportunities to optimize procurement. For example, a company can monitor category-specific trends, enabling them to identify potential savings in areas like facility maintenance or software subscriptions.
Difficulties in Spend Analysis Without UNSPSC
Without a robust classification system like UNSPSC, companies often face a range of challenges in their spend analysis efforts. First, manual classification of data is time-consuming and prone to error, making it difficult to achieve consistent categorization across departments. Moreover, inconsistencies in spend data make it harder to track, monitor, and report on procurement activities, leading to a lack of visibility into spending patterns and hindering efforts to benchmark suppliers effectively.
When spend data isn’t accurately categorized, organizations may miss opportunities for cost savings, such as consolidated purchases or volume discounts. Additionally, they may struggle with regulatory compliance, as inconsistent classification complicates audit processes and increases the likelihood of reporting errors.
Enhancing Spend Analysis with UNSPSC
To fully unlock the potential of spend analysis, companies can implement UNSPSC in several ways:
- Standardized Spend Categories
Implementing UNSPSC in spend analytics ensures that all procurement data is classified using the same system. This improves visibility across different departments and regions by creating a uniform view of spend data, making comparisons and consolidations easier. For example, a global company can standardize procurement data from various offices, enabling centralized analysis that supports strategic purchasing decisions. - Improved Spend Visibility
With UNSPSC, companies can break down spending into highly detailed categories. This granular visibility allows procurement teams to monitor specific spend areas, such as IT services or logistics, and identify opportunities for cost reductions. By isolating spend patterns, companies can reduce redundant purchases and optimize their procurement strategies. - Supplier Benchmarking
UNSPSC provides a consistent way to categorize suppliers, allowing organizations to benchmark costs for similar goods or services from different vendors. This enables companies to compare suppliers more effectively, helping them identify opportunities for cost savings or improved performance within specific categories. - Spend Control and Compliance
By categorizing spend data with UNSPSC, companies can more easily identify areas where spending exceeds budget thresholds. This system helps organizations gain better control over their procurement activities, enabling more targeted cost reduction efforts. Moreover, using standardized classifications simplifies compliance with industry-specific regulations, improving audit readiness and ensuring that procurement activities meet necessary reporting requirements. - Automated Spend Classification
When combined with AI-driven analytics platforms, UNSPSC can enable automated spend classification, reducing the need for manual efforts. AI algorithms can map purchases to the correct UNSPSC codes, ensuring real-time categorization of new transactions. This automation allows procurement teams to focus on strategic initiatives rather than getting bogged down in manual data management tasks. - Enhanced Predictive Analytics
By using UNSPSC to organize historical spend data, companies can apply predictive analytics to anticipate future procurement needs. For example, trends in past spending across categories like consulting or software licenses can inform contract negotiations or help manage inventory levels more effectively, providing a proactive approach to procurement.
How AICA Can Help Optimize UNSPSC Classification and Spend Analysis
We recognize that implementing and maintaining UNSPSC classification can be a daunting task for many organizations. That’s why AICA’s advanced AI-driven solutions are designed to support businesses in classifying their data according to the latest version of UNSPSC.
Here’s what makes AICA’s classification service unique:
- Speed and Accuracy
AICA’s AI solutions are up to 90% faster than traditional manual methods, allowing you to implement UNSPSC classifications quickly and efficiently. Our specialized algorithms ensure a classification accuracy of over 80%, far surpassing what can be achieved through manual data entry or general AI models. - Cost-Effective Data Maintenance
Maintaining an accurate and up-to-date classification system is crucial for long-term spend analysis success. AICA’s solutions automate much of the classification and data enrichment process, reducing operational costs and freeing up procurement teams to focus on higher-value tasks. - Customized Solutions
Every company’s procurement system is unique, and AICA provides customizable services to ensure that your UNSPSC implementation aligns with your specific needs. Whether you require one-time data classification or ongoing support, AICA can help you streamline your procurement activities and maximize the value of your spend analysis.
Conclusion
UNSPSC classification is more than just a tool for organizing procurement data; it’s a strategic approach to enhancing spend analytics. By implementing this system, companies can gain better visibility into their spending, improve supplier benchmarking, and control costs more effectively. AICA’s advanced AI-driven solutions can help you leverage UNSPSC classification to its full potential, ensuring that your spend data is clean, consistent, and actionable.
*This article is written by USC Consulting Group’s strategic partner in data cleansing and management, AICA. For more information how AICA can cleanse and enrich your product and services data with AI, visit their website.
Factors ranging from the weather to celebrities’ social media posts can spur the public’s demand for particular products. Those spikes can cause supply chain constraints company leaders aim to avoid. It is better when corporate teams can predict what people will want and get those products far enough in advance to cater to everyone wishing to buy them. To achieve this, businesses are using AI to strengthen their supply chains. Here’s how…
Managing Demand While Selling Diverse Product Assortments
Demand planning is especially complicated when retailers sell huge varieties of goods within a large category. Such was the case with one of Canada’s largest electronics retailers. People go there to purchase everything from phone chargers to televisions.
However, the demand for those two examples is very different. Many consumers buy several phone chargers per year, such as if they want one for each main room in a home or have forgotten to pack the item before going on a trip. However, most TVs last several years, and people only buy them once the ones they have break or otherwise no longer meet their needs. Plus, many shoppers are more likely to buy those big-ticket items during the holiday season than at other times.
The Canadian retailer uses AI and machine learning technologies to get data-driven demand insights that shape inventory and supply-chain-related decisions. Its leaders have already noticed several benefits. For example, demand planning has become more automated, and those involved can receive detailed reports highlighting potential business risks and impacts.
Additionally, supply chain employees can address slow-moving inventory, plan more enticing promotional offers and reduce stockouts. Another aspect of the AI solution evaluates various supply chain scenarios and gives prescriptive recommendations to prevent unwanted consequences. These examples show how AI can support workers in their roles and increase productivity.
A common misconception about AI is that it will replace human staff. One study found job loss from automation and other advanced technologies was a worry for 42% of respondents. However, besides assisting them with the tasks they already know, artificial intelligence can expand their skills, encouraging them to use new platforms and tools that make demand planning easier.
Streamlining Demand Planning Processes for Better Productivity
Demand planning processes vary depending on what the brand sells, the size of its supplier network, its budget and more. However, no matter how organizations handle them currently, AI can pinpoint opportunities to streamline the work for better overall outcomes.
One example comes from a multinational consumer goods enterprise offering diapers, detergent, personal grooming products and other household staples. Leaders hoped to improve current demand planning by bringing artificial intelligence into the workflow. Initial data inputs for the project included bill-of-materials information for 5,000 products and 22,000 components. Additionally, users imported various types of supporting supply chain details into the system, including specifics about vendors, warehouses and manufacturing plants.
The technology then compiles all that information to give real-time or trend-based insights. Besides providing live inventory data, the AI product can generate supply projection reports that indicate future needs while highlighting possible supply chain disruptions. Knowing about potential issues sooner gives employees the information to act confidently and prevent or mitigate those problems.
The tool was also a significant productivity booster for the consumer goods firm. For example, supply chain queries used to take more than two hours to complete but now occur immediately. Additionally, although it formerly needed more than 10 people to verify the data, the technology can do that without human oversight. Such improvements substantiate studies showing AI can make people 20%-45% more productive depending on various factors.
Running Supply Chain Simulations Before Key Events
Even though some periods of increased demand are impossible to predict, most supply chain managers can anticipate others with near certainty. For example, Black Friday is one of the biggest shopping days of the year in the United States. Additionally, late summer drives sales of bedding sets, reasonably priced furniture and school supplies as students prepare for college.
Demand planning is essential for giving supply chain professionals the necessary information to source and move the products customers will want most during those hectic periods. Since artificial intelligence can process large quantities of information quickly, users could feed details such as social media mentions, customer service email or chat data, and sales figures into tools to determine which factors make some products more or less desirable.
The leaders of one multinational American retailer used AI to determine what customers would want before Black Friday arrived. The goal was to learn those details before shoppers even consciously expressed a desire to buy specific items. While using the artificial intelligence platform, retail staff entered data about shopping and customer trends, seasonal factors and more. The resulting output steered supply chain decisions and helped address issues that might ordinarily cause Black Friday disruptions.
The retailer has also added AI to its daily supply chain workflows, relying on the technology to anticipate demand cycles and unexpected traffic peaks. Some businesses use complementing technologies such as digital twins to get similar results. These tools enable people to predict bottlenecks and investigate potential actions before pursuing them in real life.
Making Demand Planning More Manageable
Demand planning is tricky and requires a thoughtful approach from people who combine their expertise with trustworthy data. However, these examples show how purposeful AI applications can assist with this all-important aspect of supply chain operations, increasing the likelihood of satisfied customers and profit.
*This article is written by Jack Shaw. Jack is a seasoned automotive industry writer with over six years of experience. As the senior writer for Modded, he combines his passion for vehicles, manufacturing and technology with his expertise to deliver engaging content that resonates with enthusiasts worldwide.
Efficient warehouse management is crucial for the success of any business. However, numerous challenges can hinder operations and impact overall profitability. Understanding these obstacles and implementing effective solutions is essential for optimizing warehouse performance.
Common Warehousing Challenges
Ineffective warehouse management practices, such as inadequate order and inventory management, can lead to significant inefficiencies and losses. Inaccurate data, inconsistent tracking, and insufficient space further exacerbate these issues. Additionally, erratic changes in demand and economic fluctuations can disrupt operations and make it difficult to maintain optimal inventory levels. Packaging wastefulness and design shortcomings can also contribute to increased costs and environmental concerns.
Optimizing Inventory Management
To address inventory management challenges, businesses should invest in advanced technologies and streamline processes. Implementing cloud-based inventory management platforms with demand forecasting tools and automated reordering systems can help optimize stock levels and reduce carrying costs. Utilizing mobile productivity tools allows for real-time inventory tracking and control, improving efficiency and accuracy.
Enhancing Warehouse Layout and Space Utilization
Maximizing warehouse space utilization is crucial for optimizing operations and reducing costs. Implementing a well-designed warehouse layout, incorporating storage solutions that maximize vertical space, and utilizing advanced warehouse management systems can help streamline workflows and improve productivity.
Leveraging Technology and Data
Technology plays a vital role in modern warehousing. Implementing barcode technology and system-directed pick/put-away procedures can significantly improve order fulfillment accuracy and speed. Digitizing documentation and utilizing data analytics can provide valuable insights into inventory levels, customer demand, and operational performance.
Addressing Packaging and Sustainability
Packaging waste and design shortcomings can impact both costs and environmental sustainability. Collaborating with pharma packaging machine manufacturers to optimize packaging design can help reduce waste and improve efficiency. Additionally, implementing recycling programs and using sustainable packaging materials can contribute to environmental responsibility.
Overcoming warehousing challenges requires a combination of strategic planning, technological advancements, and efficient processes. By addressing issues such as inventory management, space utilization, and packaging optimization, businesses can improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. The resource below provides a visual overview of common warehousing challenges and potential solutions.
At USC Consulting Group, we’ve been empowering performance for more than 50 years. What does that mean?
It means we’re an operations management and process improvement firm that empowers your people and processes to achieve operational excellence.
The below graphic lays out our experience and the areas we specialize in:
Let’s look in more detail at how USC partners with you to accelerate and augment your process improvement efforts.
What we focus on
Operational excellence. We help clients define and implement a strategic approach to achieving and maintaining the highest levels of operational performance. It’s about eliminating waste, improving quality and ramping up productivity.
Process improvements. We look at your processes through the lens of efficiency and effectiveness. We identify bottlenecks that might be slowing down your workflow, assessing the “we’ve always done it this way” processes that every business has. We find that a fresh set of eyes on these types of long-held processes can yield more effective ways to achieve results.
Optimal efficiency. This is about the “well-oiled machine” factor. Everyone knows what that is, although it’s different for every company. It’s when you’re cooking and booking, churning and burning, and achieving the maximum throughput for your efforts.
Supply chain optimization. In the post-Covid era, we’re still seeing supply chain disruption and the headaches they cause. We help companies analyze their supply chain networks and spot inefficiencies and bottlenecks. Is there a supplier closer to home? Is it time to reshore? Can we improve procurement or logistics?
Change management. Many of the process changes we recommend involve new ways of doing things – perhaps significant changes. With training and development, strong communication and getting feedback and input from stakeholders, we can help companies embrace change for the better.
Asset Performance Management. At USC, we focus on getting the most out of the assets you already have. Heavy investments in new technology is not always necessary, especially if your old workhorses just need some care and feeding. Applying predictive maintenance to reduce unplanned downtime, usage that doesn’t cause more wear and tear than necessary, and processes to extend the lifecycle of the tools you rely on.
EBITDA improvement. This refers to a company’s Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation and Amortization. Sounds like your worst day in the accountant’s office, right? But it’s really about helping clients look for cost-savings opportunities, revenue enhancement, and more. It’s also about everything else we do – productivity improvement, asset management, operational efficiency, cost reduction and more.
How we do it
How do we enhance our clients’ operations? We’re experts in process improvement methodologies and tools, like:
Lean Six Sigma. LSS is a combination of two powerful methodologies, Lean, which focuses on limiting waste in a process, and Six Sigma, which focuses on increasing quality.
Sales, Inventory, and Operations Planning (SIOP). In a nutshell, SIOP aligns sales, inventory and operations planning functions to improve demand forecasting, efficiency, supply chain performance and more.
Employee Involvement Prototype Process. One of the cornerstone techniques USC uses to validate and measurably implement changes to elements of the MOS with full client personnel engagement. Your employees are the most vital components to every project, especially the workers in the trenches on the shop floor or production site. We involve them every step of the way.
System Reviews. We do a comprehensive analysis of your systems, processes, procedures and more. System Reviews tell the story of a company’s process and depicts the future state MOS with the deficiencies from current state corrected. It shows the flow of data, actionable information and decision-making points in a closed loop environment.
LINCS advanced reporting tools. The Lean Information Control System (LINCS) is a state-of-the-art software application that facilitate fact-based decision making from the shop floor to the boardroom. It includes modules for advanced planning, manufacturing and logistics, value stream mapping, scheduling, inventory analysis and more. Operators are able to see and evaluate their work as it takes place, while executives and managers are better equipped to prioritize activities based on accurate, actionable information.
AI, Machine Learning, and Predictive Analytics. Much like Netflix’s use of predictive analytics created a seismic shift in consumer expectations, this new technology is transforming operating procedures and processes. Predictive analytics helps companies better understand what’s occurring in any given process, refine and optimize processes, and more. But, it also needs the human touch. People aren’t getting replaced by the bots in this area any time soon. To learn more, download our free eBook: AI and Machine Learning: Predicting the Future.
Our 55-plus years of experience covers a wide variety of industries, including:
- Mining & Metals
- Food & Beverage
- Manufacturing
- Building Products
- Automotive
- Pulp & Paper
- Life Sciences
- Oil & Gas
- Utilities & Energy
- …And many more
We have a defining principle to our approach that guides every project. We do not swoop in and tell companies how to do it better.
We are partners in the process. We work with your team to implement the changes at the point of execution.
We listen to what makes your company tick, observe your current operations, get a handle on the issues, involve your frontline employees in the process, and implement a plan for change.
We play the long game, delivering results our clients can maintain for years to come. We don’t have our 98% customer satisfaction rating for nothing.
That’s how USC Consulting Group empowers YOUR performance.