-
Subscribe to Blog:
SEARCH THE BLOG
CATEGORIES
- Aerospace
- Asset Maintenance
- Automotive
- Blog
- Building Products
- Case Studies
- Chemical Processing
- Consulting
- Food & Beverage
- Forestry Products
- Hospitals & Healthcare
- Knowledge Transfer
- Lean Manufacturing
- Life Sciences
- Logistics
- Manufacturing
- Material Utilization
- Metals
- Mining
- News
- Office Politics
- Oil & Gas
- Plastics
- Private Equity
- Process Improvement
- Project Management
- Spend Management
- Supply Chain
- Uncategorized
- Utilities
- Whitepapers
BLOG ARCHIVES
- July 2025 (1)
- June 2025 (4)
- May 2025 (1)
- April 2025 (1)
- March 2025 (1)
- February 2025 (4)
- January 2025 (4)
- December 2024 (4)
- November 2024 (2)
- October 2024 (6)
- September 2024 (5)
- August 2024 (5)
- July 2024 (6)
- June 2024 (3)
- May 2024 (3)
- April 2024 (4)
- March 2024 (3)
- February 2024 (4)
- January 2024 (5)
- December 2023 (2)
- November 2023 (1)
- October 2023 (6)
- September 2023 (3)
- August 2023 (4)
- July 2023 (2)
- June 2023 (3)
- May 2023 (7)
- April 2023 (3)
- March 2023 (3)
- February 2023 (5)
- January 2023 (6)
- December 2022 (2)
- November 2022 (5)
- October 2022 (5)
- September 2022 (5)
- August 2022 (6)
- July 2022 (3)
- June 2022 (4)
- May 2022 (5)
- April 2022 (3)
- March 2022 (5)
- February 2022 (4)
- January 2022 (7)
- December 2021 (3)
- November 2021 (5)
- October 2021 (3)
- September 2021 (2)
- August 2021 (6)
- July 2021 (2)
- June 2021 (10)
- May 2021 (4)
- April 2021 (5)
- March 2021 (5)
- February 2021 (3)
- January 2021 (4)
- December 2020 (3)
- November 2020 (3)
- October 2020 (3)
- September 2020 (3)
- August 2020 (4)
- July 2020 (3)
- June 2020 (5)
- May 2020 (3)
- April 2020 (3)
- March 2020 (4)
- February 2020 (4)
- January 2020 (4)
- December 2019 (3)
- November 2019 (2)
- October 2019 (4)
- September 2019 (2)
- August 2019 (4)
- July 2019 (3)
- June 2019 (4)
- May 2019 (2)
- April 2019 (4)
- March 2019 (4)
- February 2019 (5)
- January 2019 (5)
- December 2018 (2)
- November 2018 (2)
- October 2018 (5)
- September 2018 (4)
- August 2018 (3)
- July 2018 (2)
- June 2018 (4)
- May 2018 (3)
- April 2018 (3)
- March 2018 (2)
- February 2018 (2)
- January 2018 (1)
- December 2017 (1)
- November 2017 (2)
- October 2017 (2)
- September 2017 (1)
- August 2017 (2)
- July 2017 (2)
- June 2017 (1)
- April 2017 (3)
- March 2017 (3)
- February 2017 (2)
- January 2017 (2)
- December 2016 (2)
- November 2016 (4)
- October 2016 (4)
- September 2016 (3)
- August 2016 (6)
- July 2016 (4)
- June 2016 (4)
- May 2016 (1)
- April 2016 (3)
- March 2016 (4)
- February 2016 (2)
- January 2016 (4)
- December 2015 (3)
- November 2015 (3)
- October 2015 (1)
- September 2015 (1)
- August 2015 (4)
- July 2015 (6)
- June 2015 (4)
- May 2015 (7)
- April 2015 (6)
- March 2015 (6)
- February 2015 (4)
- January 2015 (3)
CONNECT WITH US
Tag Archives: Material Handling
Statistical process control (SPC) is a commonly used machine learning software in manufacturing that measures the consistency of a product’s performance based on its design specifications. Minimizing variability is a crucial part of avoiding defects and maintaining resilient manufacturing operations.
This guide outlines the different ways that businesses can effectively utilize SPC and reap all of the benefits this technology has to offer.
How Statistical Process Control Works
SPC is a tried and true technology that businesses have been using for more than 100 years to improve their manufacturing operations. It conducts ongoing statistical analyses, taking into account factors such as the materials, design, employees who handled the product and the machinery used to create the product.
SPC’s constant vigilance enables businesses to make swift and accurate resolutions to quality control problems. However, it’s not fully autonomous like other manufacturing software that can identify statistical correlations without human help. Instead, it relies on large amounts of training datasets that another source must manually input to achieve the desired results.
This form of machine learning is known as supervised learning. Businesses can input human-labeled datasets by themselves, or they can recruit another algorithm to automatically input statistics in a process called “machine annotation.” In either case, SPC needs to absorb as much raw data as possible to maximize its efficiency.
SPC displays its findings in easy-to-read control charts, and it’s the business’s responsibility to set the parameters for each chart by providing the software with enough information. This process includes six basic steps:
- Define the manufacturing process you want to monitor and control by establishing the input variables, output variables, equipment, materials and any other external factors that might affect the process.
- Collect the data that the software extrapolated from the variables you provided, then organize it into a digestible format — usually a chart or spreadsheet.
- Select and construct the control charts based on the type of data you’re using, such as weight, length, temperature and any defects that might have occurred.
- Look for patterns in the control charts that indicate special cause variations in performance due to underlying defects. You can calculate process variability through a capability index, such as C, Cpk, Pp and PPk.
- Investigate the root causes of the variations and make the necessary equipment, material or operational adjustments to correct them.
- Continue to collect and organize data to identify more variations, updating the control specifications as needed.
This process sounds awfully similar to Statistical Quality Control (SQC), but there are some key differences. Statistical Process Control measures independent variables, while SQC strictly focuses on dependent process outputs. SQC also carries out acceptance tests by screening individual product samples, while SPC relies on large datasets and doesn’t have an acceptance testing feature.
Types of SPC Tools
Many types of analysis tools have developed during SPC’s century-long evolution. These tools are split into two main categories — basic tools of quality (7-QC tools) and supplemental tools (7-SUPP tools). Here’s a quick rundown of how businesses can use the 7-QC tools:
- Stratification: separating data into subcategories by unique characteristics to clarify the origins of an existing problem.
- Histogram: A bar graph that displays the frequency of variability and the most common offenders.
- Check sheet: A document with tabular or metric format that tracks the number of special cause variations.
- Cause-and-effect diagram: A chart that shows all of the factors that lead to special cause variations and draws potential correlations between them.
- Scatter diagram: A dotted diagram that displays the overlap between dependent variables on the y-axis and independent variables on the x-axis.
- Control chart: A line-based graph that shows processes’ stability levels and pinpoints the likely variation within produced items.
- Pareto chart: This chart applies the 80/20 principle — 20% of variables cause 80% of problems — to display the most common causes of manufacturing failures.
Stratification also often appears in the 7-SUPP tools category because of its versatility and importance to statistical analysis. Breaking up large datasets into smaller digestible chunks makes SPC software more accurate at identifying problems and reducing variability. Here are the other six 7-SUPP tools:
- Flowchart: A straightforward diagram that outlines the step-by-step process of a manufacturing sequence.
- Defect mapping: A chart that shows the different types of known product flaws within a business’s manufacturing operations.
- Events logs: A variable summary showing the chain of events that resulted from an undesired occurrence.
- Progress centers: Centralized locations dedicated to tracking improvements and supporting informed decision making.
- Randomization: The deployment of random manual and automated input variables to eliminate human bias.
- Sample size determination: Choosing the number of subjects to include in a representative group when tracking manufacturing trends.
Today’s SPC software modules include all of these tools, allowing businesses to access dashboards that display the various charts and diagrams in one place. These insights can lead to identification of quantifiable improvement opportunities that maximize operational efficiency.
Benefits of Using SPC
SPC is one of the most effective machine learning resources for achieving consistent performance in manufacturing operations. Eliminating process errors allows businesses to simultaneously address the three biggest challenges in material handling — workplace hazards, equipment damage and carbon emissions — in many ways:
- Reduces manufacturing costs
- Monitors employee productivity
- Improves resource utilization
- Optimizes manual inspections
- Reduces rework and warranty claims
When these benefits combine, the final result is a more satisfied client base and a more profitable business. While SPC software can’t do all of the inspection work on its own, the tools and insights it provides are invaluable in a manufacturing environment.
Use Statistical Process Control to Its Full Potential
Business leaders who are willing to put in the necessary effort to provide SPC software with large datasets can use this technology to its full potential. They will gain access to numerous eye-opening statistics about operational inefficiencies and have all the knowledge they need to make accurate adjustments.
*This article is written by Jack Shaw. Jack is a seasoned automotive industry writer with over six years of experience. As the senior writer for Modded, he combines his passion for vehicles, manufacturing and technology with his expertise to deliver engaging content that resonates with enthusiasts worldwide.
The material handling industry is the backbone of globalized supply chains. However, it encounters a range of challenges, both internal and external. One notable external challenge is the impact of labor shortages on transportation and logistics, which are vital components of material handling operations.
To overcome these challenges, companies are making significant investments in technology. According to the 2023 MHI Annual Industry Report, 74% of supply chain leaders are increasing technology spending.
While capitalizing on advanced supply chain technologies can offer some respite, leaders may need to take more profound measures to effectively address the emerging issues.
In light of the survey responses featured in the MHI report, this article aims to explore the three primary challenges faced by the material handling industry.
#1: Worker safety
According to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics, there were 5,190 fatal work injuries in 2021, with 798 attributed to exposure to harmful materials or the environment — the highest figure since the series began in 2011!
Material handling operations often involve risky conditions for workers. From handling hazardous chemicals in facilities to lifting heavy loads in warehouses, workers in this supply chain sector regularly risk their health and lives.
Common causes of worker injuries in material handling include:
- improperly stored materials falling
- damaged storage units
- heavy manual lifting, pushing, or carrying
- exceeding loading limits on lifting equipment
- collision with materials or equipment.
Ensuring workers’ safety and security is vital and requires a multi-pronged approach. Safety negligence or violation can quickly become a compliance issue, resulting in monetary and reputational damage.
Material handling and supply chain companies address workplace safety challenges by providing personal protective equipment (PPE), delivering safety training, conducting equipment training, and performing safety audits.
Conscious companies that rely on manual labor also address the ergonomics of material handling in their safety training. Identifying ergonomic risk factors in manual or machine-supported lifting, carrying, and pushing jobs is critical for preventing fatigue and injury.
To prioritize the health and safety of their employees, conscious companies cultivate a “safety-first” culture. A prime example of a logistics company that excels in worker safety is DHL, based in Germany.
Safety is a core value for DHL, and they have implemented a holistic approach to address safety concerns through continuous training, strict compliance with regulations, and active employee engagement.
#2: Material and equipment damages
Poorly maintained equipment, untrained workers, and natural disasters can lead to expensive damages. Among these challenges, equipment damage stands out as one of the primary concerns for material handling companies, often resulting in downtime. In fact, unplanned downtime costs manufacturers a staggering $50 billion annually.
To ensure reliability and resilience, timely maintenance is crucial for all aspects of material handling operations, ranging from trucks and forklifts to pallets and sliding racks.
Similarly, it is equally important to prevent damage to the materials being handled by the equipment or workers. Well-organized warehouse loading and unloading processes, supported by well-trained workers and advanced technology, can effectively minimize material handling damages.
Many supply chain companies are leaning towards predictive maintenance solutions for equipment to ensure they are well-maintained for operations. Predictive maintenance leverages technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to predict potential problems with equipment and fleet.
In addition, these companies are minimizing accidents that result in costly damages through increased visibility. Warehouse inventory management and organization technology, for example, helps maintain optimal inventory levels, prevents overstocking, and ensures efficient use of storage space.
Gradesens, a Swiss company specializing in predictive maintenance, is helping logistics companies with very-narrow aisle warehouses proactively maintain automated systems for loading and unloading. With accurate and timely maintenance, the warehouses prevent downtime because of equipment failure.
#3: Controlling emissions
Carbon emissions are a huge problem for major industries, and material handling is no exception. With environmental organizations ringing alarm bells on rising global temperatures, material handling and supply chain leaders are paying close attention to sustainability.
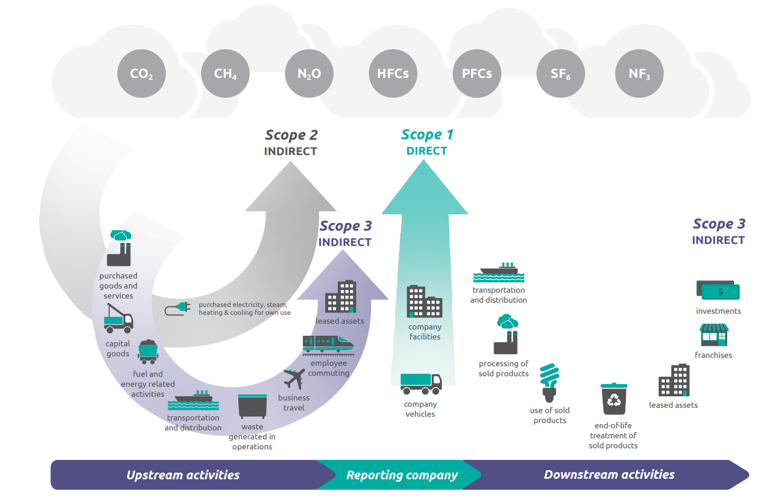
Material handling operations, including warehousing, contribute to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions through electricity usage, particularly natural gas. Additionally, using fossil fuel-powered vehicles and equipment contributes significantly to carbon emissions. Many material handling companies make up Scope 3 emissions for other organizations.
Fortunately, the material handling industry is adopting energy-efficient practices, thanks to environmental advocacy and pressure from governments with ambitious sustainability goals.
The MHI report revealed that organizations in material handling are investing in electrification, natural resource management, sustainable water consumption, and the transition to renewable energy.
Similarly, the European Logistics Supply Chain Sustainability Report found that 80% of surveyed companies consider sustainability a key focus area.
Material handling companies are reducing carbon footprint by investing in electric lift trucks. Electric forklifts have zero emissions compared to their counterparts powered by internal combustion engines.
Renewable energy has also been a focus for the industry, with major companies setting goals to go 100% carbon-neutral or net zero emissions. For instance, Amazon, the largest corporate buyer of renewable energy, uses clean energy in many fulfillment centers. The company plans to reach its 100% renewable energy goal by 2025.
The takeaway
Material handling is linked with virtually every industry, which makes its challenges essentially every industry’s challenges.
Some of the issues aren’t unique to material handling. For instance, sustainability is a global issue. The good news is that many companies are taking promising measures to combat these challenges: and technology is at the heart of these solutions.
It’s imperative for organizations in material handling to provide training and maintain equipment for better worker safety. Similarly, investing in clean energy solutions can go a long way in reducing emissions, which is good for the environment and business.

Matilda Odell
*This article is written by Matilda Odell. Matilda works as the Content Creation Specialist at the brand TAWI, a brand by Piab Group, which enables smart lifting optimized for people and businesses. Piab helps its customers to grow by transforming their businesses with increased automation. If you have any questions about lifting equipment such as vacuum lifters or other lifting devices, Matilda is the person to talk to.
Studies have shown that over 40% of workers across various industries spend a significant portion of their workweek on repetitive manual tasks. In the manufacturing sector, these tasks often involve data collection and manual data entry, which many consider to be inefficient given the availability of advanced automation software in today’s market.
Innovative automation programs are designed to automatically collect, upload, or synchronize data into a system of record. This automation can help eliminate production bottlenecks and streamline manufacturing processes, ultimately improving output. Moreover, automation can significantly reduce the risk of human error, which can lead to injuries. In fact, a majority of workers (nearly 60%) believe that they could save six or more hours per week if the repetitive aspects of their jobs were automated.
Automation is not limited to the field personnel, as managers are also looking to streamline their own tasks. A renowned technological research and consulting firm predicts that by 2024, 69% of day-to-day managerial work will be fully automated. Examples of automatable managerial tasks include approvals, sign-offs, status updates, and confirmation requests. Increased efficiency in these operations can free up time for employees at all levels to contribute more strategically to the success of a business.
In addition to automation, cutting-edge robotic technology is also being utilized in many manufacturing organizations. Programmed robots or robot-controlled machines that use artificial intelligence (AI) can enhance a company’s assembly, material handling, and processing capabilities. Robots excel in predictable environments and can handle physically demanding or monotonous tasks that may negatively impact employee well-being or morale. This results in increased productivity and reduced labor costs.
Another type of robot gaining popularity is the collaborative robot, or cobot, which is specifically designed for direct human-robot interaction. Cobots are relatively new but are projected to have exponential growth in the market, with an estimated worth of nearly $2 billion by 2026, up from $590.5 million in 2020. Industry experts predict that by 2025, 34% of industrial robots sold will be cobots. Cobots are cost-effective, safe, and flexible, making them an ideal tool for small and mid-sized manufacturers to modernize their operations, reduce redundant tasks, improve productivity, and achieve peak performance.
To learn more about the impact of repetitive tasks in manufacturing and how technology can counter them, please refer to the infographic below:
Repetitive Tasks in Manufacturing from Acieta, a manufacturing robotic company