-
Subscribe to Blog:
SEARCH THE BLOG
CATEGORIES
- Aerospace
- Asset Maintenance
- Automotive
- Blog
- Building Products
- Case Studies
- Chemical Processing
- Consulting
- Food & Beverage
- Forestry Products
- Hospitals & Healthcare
- Knowledge Transfer
- Lean Manufacturing
- Life Sciences
- Logistics
- Manufacturing
- Material Utilization
- Metals
- Mining
- News
- Office Politics
- Oil & Gas
- Plastics
- Private Equity
- Process Improvement
- Project Management
- Spend Management
- Supply Chain
- Uncategorized
- Utilities
- Whitepapers
BLOG ARCHIVES
- June 2025 (4)
- May 2025 (1)
- April 2025 (1)
- March 2025 (1)
- February 2025 (4)
- January 2025 (4)
- December 2024 (4)
- November 2024 (2)
- October 2024 (6)
- September 2024 (5)
- August 2024 (5)
- July 2024 (6)
- June 2024 (3)
- May 2024 (3)
- April 2024 (4)
- March 2024 (3)
- February 2024 (4)
- January 2024 (5)
- December 2023 (2)
- November 2023 (1)
- October 2023 (6)
- September 2023 (3)
- August 2023 (4)
- July 2023 (2)
- June 2023 (3)
- May 2023 (7)
- April 2023 (3)
- March 2023 (3)
- February 2023 (5)
- January 2023 (6)
- December 2022 (2)
- November 2022 (5)
- October 2022 (5)
- September 2022 (5)
- August 2022 (6)
- July 2022 (3)
- June 2022 (4)
- May 2022 (5)
- April 2022 (3)
- March 2022 (5)
- February 2022 (4)
- January 2022 (7)
- December 2021 (3)
- November 2021 (5)
- October 2021 (3)
- September 2021 (2)
- August 2021 (6)
- July 2021 (2)
- June 2021 (10)
- May 2021 (4)
- April 2021 (5)
- March 2021 (5)
- February 2021 (3)
- January 2021 (4)
- December 2020 (3)
- November 2020 (3)
- October 2020 (3)
- September 2020 (3)
- August 2020 (4)
- July 2020 (3)
- June 2020 (5)
- May 2020 (3)
- April 2020 (3)
- March 2020 (4)
- February 2020 (4)
- January 2020 (4)
- December 2019 (3)
- November 2019 (2)
- October 2019 (4)
- September 2019 (2)
- August 2019 (4)
- July 2019 (3)
- June 2019 (4)
- May 2019 (2)
- April 2019 (4)
- March 2019 (4)
- February 2019 (5)
- January 2019 (5)
- December 2018 (2)
- November 2018 (2)
- October 2018 (5)
- September 2018 (4)
- August 2018 (3)
- July 2018 (2)
- June 2018 (4)
- May 2018 (3)
- April 2018 (3)
- March 2018 (2)
- February 2018 (2)
- January 2018 (1)
- December 2017 (1)
- November 2017 (2)
- October 2017 (2)
- September 2017 (1)
- August 2017 (2)
- July 2017 (2)
- June 2017 (1)
- April 2017 (3)
- March 2017 (3)
- February 2017 (2)
- January 2017 (2)
- December 2016 (2)
- November 2016 (4)
- October 2016 (4)
- September 2016 (3)
- August 2016 (6)
- July 2016 (4)
- June 2016 (4)
- May 2016 (1)
- April 2016 (3)
- March 2016 (4)
- February 2016 (2)
- January 2016 (4)
- December 2015 (3)
- November 2015 (3)
- October 2015 (1)
- September 2015 (1)
- August 2015 (4)
- July 2015 (6)
- June 2015 (4)
- May 2015 (7)
- April 2015 (6)
- March 2015 (6)
- February 2015 (4)
- January 2015 (3)
CONNECT WITH US
Tag Archives: Asset Performance Management
Over the next five years, mining and metals companies are expected to spend between $25 billion to $30 billion annually to maintain their assets.
Largely driven by efforts to improve operational efficiency, reduce downtime, immediately reduce costs, meet sustainability goals, and manage operational risks in an increasingly volatile market, mining and metals executives are motivated to start their asset management transformation now. Delaying this transformation could result in lost competitive advantages, higher operational costs, and increased regulatory or market pressures.
Over the next five years, the mining and metals industry is projected to invest heavily in the maintenance of fixed and mobile assets. Various reports indicate that the industry is expected to allocate a significant portion of its CAPEX to maintaining and upgrading its assets. A substantial part of this investment will be directed toward maintaining critical assets required to meet global demand for minerals essential for the energy transition. In a recent survey conducted by Global Data, 48% of the companies surveyed indicated they plan to increase investments in technologies like AI and IoT sensors for equipment upkeep over the next two years.
Investment in predictive maintenance is becoming a top priority for many mining operations. Companies are leveraging their EAM’s with advancing technologies like Digital Twins, AI and IoT, along with other reliability and planning applications, and significantly transforming asset management and the asset lifecycle. These advancements in technology are expected to reduce maintenance costs by 20-30%.
Mining and metals companies integrating Enterprise Asset Management (EAM), Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS), AI, and IoT are experiencing several quantifiable benefits, including:
- Improved Asset Reliability and Uptime: Utilizing a combination of AI, IoT sensors and Digital Twins provides continuous real-time monitoring of equipment health allowing companies to predict potential failures before they occur while reducing the reliance on reactive and scheduled maintenance – reducing unplanned downtime and fewer equipment breakdowns, increasing equipment availability and extending asset lifecycles.
- Cost Reduction: A predictive maintenance capability helps avoid costly emergency repairs and reduces unnecessary scheduled maintenance, saving on labor and spare parts. It also ensures that the right parts are available when needed, minimizing overstock and understock issues, which helps reduce capital expenditure tied to inventory. It optimizes the energy usage of equipment by adjusting operational parameters in real-time, leading to lower energy consumption.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Leveraging these technologies together, allows companies to scale their asset management strategies as they grow, adapting to changes in operational needs without significant disruptions. Maintenance scheduling based on asset condition rather than time-based intervals, ensures that resources are used effectively, reducing downtime and improving workflow efficiency. They provide a holistic view of all assets, enabling better coordination between teams while improving “wrench-time” productivity and the execution of maintenance and operational tasks. It delivers a single platform to access real-time data across the entire asset portfolio, improving visibility and control over operations for optimizing performance and recommendations for future operations.
USC partners with your organization and coaches your people to significantly impact performance outcomes and accelerate Operational Excellence
USC brings a tailored, structured, and disciplined methodology, along with a range of tools and techniques we apply collaboratively with client’s personnel. Whatever your challenge, we are the people who work with our clients to find full potential and unlock the hidden value.
USC help to identify waste, redundancies, and ineffective processes, and then rapidly recover the prioritized opportunities, and convert them to improvements in performance and operating profit. Further, our people embed with client teams to develop, enhance, prototype, validate and implement asset management strategies to drive, sustain and perpetuate improvements in asset lifecycles and equipment reliability, while changing how plans, schedules, and work is executed. In short, USC implements measurable, sustainable changes that drive asset performance and financial improvements.
- Increased Wrench Time (up to 25% improvement) – Reducing non-productive time through improved work-order generation and prioritization, maintenance teams spend less time searching for work-orders, tracking down parts or waiting for approvals.
- Reduction in Travel & Downtime (up to 20% time savings) – Optimizing the routing and scheduling of maintenance tasks and reducing travel time between jobs to maximize “time on tools”.
- Faster Work-order Completion (up to 30% efficiency gains) – Reducing delays in task assignment, approval and completion tracking, technicians can move quickly from one job to the next by ensuring all the necessary tools and parts are available at the work site, eliminating delays caused by missing resources.
- Optimized Spare Parts Management (up to 15% time reduction) – Faster access to parts and accurate spare part forecasting reduce time on sourcing, stocking and searching while ensuring tools & parts are available for tasks.
- Better Data-Driven Decision Making (up to 20% longer asset life spans) – Collecting and analyzing needed information provides actionable insights that support planning and allow for more informed and pro-active decision making, often delaying the need for capital-intensive replacements.
USC clients experience measurable operational and financial results that significantly improve both the efficiency and profitability of their operations. Benefits delivered may include a 10-20% increase in overall equipment availability due to reduced unplanned downtime and optimized maintenance schedules and a 10-15% improvement in equipment utilization as predictive maintenance reduces the time equipment is out of service.
USC Helps You Tackle Key Challenges
- Optimize maintenance strategies and increase equipment availability operational output
- Predict asset integrity and reliability needs and improve time on tools
- Mitigate risks through stronger stakeholder partnerships, while removing redundancies in the supply chain
- Overcoming cultural and communication issues with contractors, while ensuring quality expectations
Do you want to understand how prepared your company is to drive needed asset management performance and reliability improvements and what the key focus areas that will contribute to lower operating costs? Contact us today.
At USC Consulting Group, we’ve been empowering performance for more than 50 years. What does that mean?
It means we’re an operations management and process improvement firm that empowers your people and processes to achieve operational excellence.
The below graphic lays out our experience and the areas we specialize in:
Let’s look in more detail at how USC partners with you to accelerate and augment your process improvement efforts.
What we focus on
Operational excellence. We help clients define and implement a strategic approach to achieving and maintaining the highest levels of operational performance. It’s about eliminating waste, improving quality and ramping up productivity.
Process improvements. We look at your processes through the lens of efficiency and effectiveness. We identify bottlenecks that might be slowing down your workflow, assessing the “we’ve always done it this way” processes that every business has. We find that a fresh set of eyes on these types of long-held processes can yield more effective ways to achieve results.
Optimal efficiency. This is about the “well-oiled machine” factor. Everyone knows what that is, although it’s different for every company. It’s when you’re cooking and booking, churning and burning, and achieving the maximum throughput for your efforts.
Supply chain optimization. In the post-Covid era, we’re still seeing supply chain disruption and the headaches they cause. We help companies analyze their supply chain networks and spot inefficiencies and bottlenecks. Is there a supplier closer to home? Is it time to reshore? Can we improve procurement or logistics?
Change management. Many of the process changes we recommend involve new ways of doing things – perhaps significant changes. With training and development, strong communication and getting feedback and input from stakeholders, we can help companies embrace change for the better.
Asset Performance Management. At USC, we focus on getting the most out of the assets you already have. Heavy investments in new technology is not always necessary, especially if your old workhorses just need some care and feeding. Applying predictive maintenance to reduce unplanned downtime, usage that doesn’t cause more wear and tear than necessary, and processes to extend the lifecycle of the tools you rely on.
EBITDA improvement. This refers to a company’s Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation and Amortization. Sounds like your worst day in the accountant’s office, right? But it’s really about helping clients look for cost-savings opportunities, revenue enhancement, and more. It’s also about everything else we do – productivity improvement, asset management, operational efficiency, cost reduction and more.
How we do it
How do we enhance our clients’ operations? We’re experts in process improvement methodologies and tools, like:
Lean Six Sigma. LSS is a combination of two powerful methodologies, Lean, which focuses on limiting waste in a process, and Six Sigma, which focuses on increasing quality.
Sales, Inventory, and Operations Planning (SIOP). In a nutshell, SIOP aligns sales, inventory and operations planning functions to improve demand forecasting, efficiency, supply chain performance and more.
Employee Involvement Prototype Process. One of the cornerstone techniques USC uses to validate and measurably implement changes to elements of the MOS with full client personnel engagement. Your employees are the most vital components to every project, especially the workers in the trenches on the shop floor or production site. We involve them every step of the way.
System Reviews. We do a comprehensive analysis of your systems, processes, procedures and more. System Reviews tell the story of a company’s process and depicts the future state MOS with the deficiencies from current state corrected. It shows the flow of data, actionable information and decision-making points in a closed loop environment.
LINCS advanced reporting tools. The Lean Information Control System (LINCS) is a state-of-the-art software application that facilitate fact-based decision making from the shop floor to the boardroom. It includes modules for advanced planning, manufacturing and logistics, value stream mapping, scheduling, inventory analysis and more. Operators are able to see and evaluate their work as it takes place, while executives and managers are better equipped to prioritize activities based on accurate, actionable information.
AI, Machine Learning, and Predictive Analytics. Much like Netflix’s use of predictive analytics created a seismic shift in consumer expectations, this new technology is transforming operating procedures and processes. Predictive analytics helps companies better understand what’s occurring in any given process, refine and optimize processes, and more. But, it also needs the human touch. People aren’t getting replaced by the bots in this area any time soon. To learn more, download our free eBook: AI and Machine Learning: Predicting the Future.
Our 55-plus years of experience covers a wide variety of industries, including:
- Mining & Metals
- Food & Beverage
- Manufacturing
- Building Products
- Automotive
- Pulp & Paper
- Life Sciences
- Oil & Gas
- Utilities & Energy
- …And many more
We have a defining principle to our approach that guides every project. We do not swoop in and tell companies how to do it better.
We are partners in the process. We work with your team to implement the changes at the point of execution.
We listen to what makes your company tick, observe your current operations, get a handle on the issues, involve your frontline employees in the process, and implement a plan for change.
We play the long game, delivering results our clients can maintain for years to come. We don’t have our 98% customer satisfaction rating for nothing.
That’s how USC Consulting Group empowers YOUR performance.
Downtime – the dreaded halt in production that can cripple a manufacturing operation. It’s more than just an inconvenience; it’s a hidden cost that can eat away at your profits. A recent study revealed that nearly 82% of businesses have experienced unexpected downtime in the past three years, with the average incident lasting four hours and costing a staggering $2 million. The impact goes beyond just financial losses – downtime can disrupt customer deliveries, delay critical projects, and erode trust with clients.
The Potential Culprits
One major factor is neglecting preventive maintenance. Regular servicing not only keeps equipment functioning smoothly but also allows technicians to identify potential problems before they snowball into major breakdowns.
Another hidden source is outdated equipment. Obsolete machinery can be a drag on your entire production line. Imagine a slow, malfunctioning piece of equipment holding up the entire process. This can put undue stress on other machines, leading to premature wear and tear, and ultimately, more downtime. Upgrading to newer, more efficient models can significantly improve production flow and reduce the risk of breakdowns. Outdated software can also be a culprit. Running outdated software can lead to compatibility issues with newer systems and leave your facility vulnerable to security breaches.
Beyond equipment and software, a lack of proper training for your workforce can also contribute to downtime. If operators don’t fully understand how a machine works, they might misuse it, leading to errors and breakdowns. Investing in comprehensive training empowers your employees with the knowledge and skills they need to operate machinery safely and efficiently, minimizing the risk of operator-induced downtime.
Finally, the importance of data tracking cannot be overstated. Keeping detailed logs of equipment issues and production hiccups allows you to identify recurring problems and implement preventative measures. Think of it as a historical record that helps you anticipate and address potential bottlenecks before they derail your production schedule.
Finding the Right Solution for You
The good news is that there are steps you can take to combat downtime and keep your production lines humming. Conducting risk audits to identify potential problems, installing sensors to monitor equipment health (like a torque transducer that detects excessive force on a rotating shaft), and implementing a comprehensive preventive maintenance program are all crucial steps in the battle against downtime.
Investing in employee training and partnering with reliable third-party service providers can further strengthen your defenses. By adopting a proactive approach to maintenance and addressing the root causes of downtime, you can significantly reduce disruptions and ensure your manufacturing operation runs smoothly and efficiently.
Want to learn more about the specific costs associated with different downtime causes? The following infographic breaks down the financial impact of various downtime triggers, helping you identify areas for improvement and optimize your production process for maximum uptime.
Mining and metals companies are implementing a range of strategies to enhance asset management and equipment reliability.
In today’s market, many senior executives leading natural resource companies hesitate in making additional capital investment and instead focus on what can be done to squeeze higher performance out of current assets. Consequently, companies are increasingly looking for ways to improve performance and returns with existing infrastructure.
The key approach to this challenge lies in upgrading and improving asset management capabilities. Many organizations have failed to deploy optimal asset management practices. This is surprising given that asset spend frequently represents 30% to 50% of the overall operating expenses. Shifting to a best-in-class asset management program will consistently deliver improved plant or equipment performance, lower operating costs, extend asset life, and generate a higher return on capital. Most recently, companies have sought to implement a range of strategies such as:
- Implementing Asset Management Systems: Utilizing robust asset management systems to track equipment performance, maintenance history, and lifecycle costs, allowing for better decision-making regarding repairs, replacements, and upgrades. Digital technologies like IoT sensors, AI-driven analytics, and automation further optimize asset management.
- Enhancing Maintenance Practices: Implementing proactive maintenance strategies like conditioned-based monitoring and reliability-centered maintenance to address issues before they cause failures. Utilizing data-driven insights, mining companies can optimize “time on tools” by identifying patterns and trends in equipment usage, maintenance needs, and performance. This allows for more precise scheduling of maintenance tasks, reducing downtime and maximizing the time equipment is operational.
- Investing in Training: Providing comprehensive training programs for front-line management, maintenance and operations personnel to ensure equipment is used and serviced properly, reducing the likelihood of breakdowns due to human error and that access to equipment is available. Training personnel to utilize data-driven insights enables management to make informed decisions impacting “time on tools” and leading to improved equipment utilization and overall operational performance.
- Improving Supply Chain Management: Ensuring timely access to quality spare parts and materials to minimize downtime caused by equipment breakdowns and repairs. Some are adopting blockchain for transparent supply chain management and better tracking of assets throughout their lifecycle.
The level of performance improvement companies can realize by implementing key strategies such as enhancing proactive maintenance practices, investing in training to improve skills and capabilities, improving supply chain management, and leveraging digital technologies and data-driven insights varies depending upon factors like current operational efficiency, the scale of implementation, and industry conditions. However, many can expect significant improvements in:
- Safety: Proper training programs and proactive maintenance strategies contribute to a safe work environment by reducing risk of accidents and equipment failures.
- Productivity: Proactive maintenance and digital technologies can reduce downtime, increase equipment availability, and optimize process execution, leading to higher productivity levels.
- Cost Reduction: Efficient equipment usage and maintenance practices can lower operational costs by minimizing unplanned downtime, reducing repair and replacement expenses, and optimizing resource utilization.
- Quality: Improving the essential management skills and work place practices result improve the quality of maintenance execution.
Overall, these strategies can result in substantial performance improvements, enhancing competitiveness and profitability for mining and metals companies.
USC Consulting Group partners with your organization and coaches your people to significantly impact performance outcomes and accelerate Asset Management and Reliability Excellence.
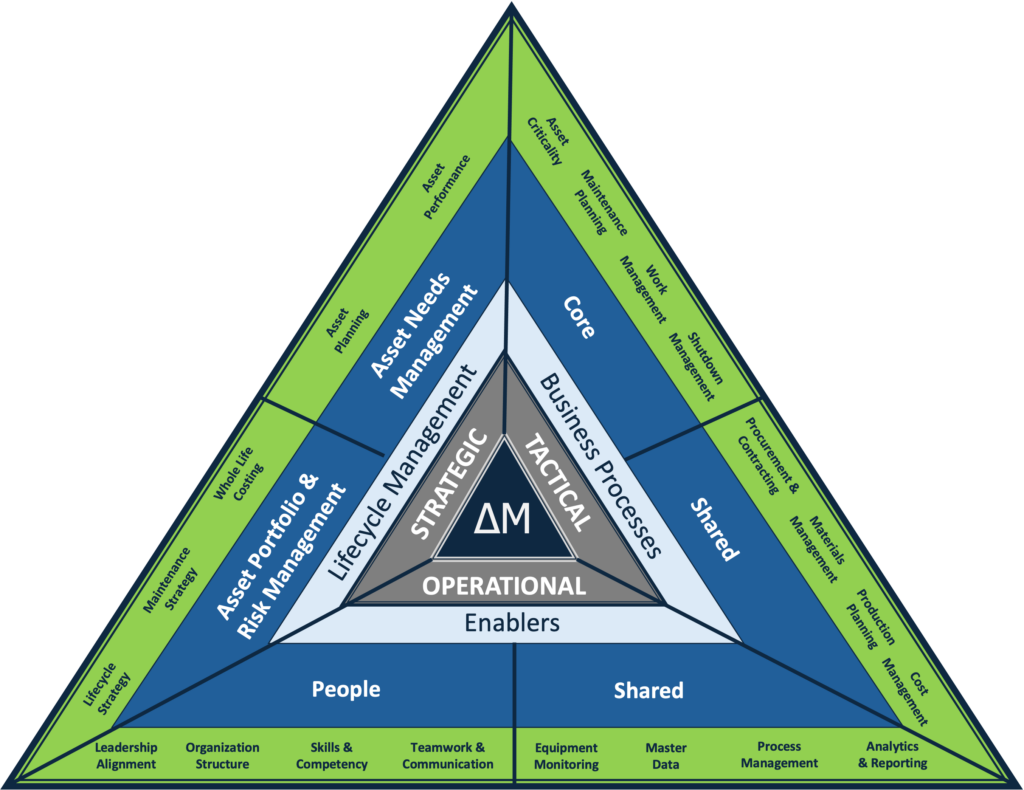
USC’s experience helping clients to shift asset performance by transforming and optimizing asset management capabilities and processes has repeatedly demonstrated the need to focus on the key levers and enablers to asset management and reliability excellence. Our asset management framework is designed to be pragmatic rather than conceptual, thereby leading to accurate, practical decisions about a client’s assets and aspirational outcomes.
The primary goal of USC’s asset management framework is to help our clients to implement and execute of a robust set of integrated processes and tools to manage and maintain their operational assets at the targeted service levels while optimizing life-cycle costs and asset life. This is accomplished by recognizing the needs to:
- Improve safe execution of work
- Increase asset life and reliability
- Improve productivity and cost performance
- Improve operational predictability
- Control material asset risks
- Develop competitive advantage
Our asset management and reliability framework helps clients identify an organization’s asset management maturity level and the areas and gaps that need to be addressed, by evaluating their strategic, tactical and operational levers and the enablers that comprise each.
Strategic (Lifecycle Management): A tailored maintenance program for each piece of equipment translates overall strategic objectives into executable plans for equipment upkeep. Our framework helps to structure and prioritize critical assets while defining a baseline operational ‘plan of action’ by determining strategies for maintaining equipment based on analysis of equipment capabilities, required performance levels, failure frequencies, and cost objectives. Optimal maintenance strategies are frequently a blend of preventative, predictive, operator-maintained, and run-to-fail options.
Tactical (Business Processes): Business processes bridge the gaps between the initial, ideal plan and the reality of ‘day-to-day’ operations, so the maintenance and reliability organization can make adjustments. Historically, many maintenance organizations have been poor utilizers of labor resources that result in low “time on tools” and excessive delays in repairing down or poor performing equipment.
Operational (Enablers): Enablers help to identify needed support to manage assets throughout their lifecycle in alignment with organizational aspirations. Leading asset management teams have also made changes in their organization structures and management practices to foster more action-oriented leadership that focuses on operational excellence, which usually requires a culture shift that must be relentlessly supported by the leadership team over the long-term. A heavy emphasis on management behaviors and company culture can help organizations make this difficult transition.
USC Helps You Tackle Key Challenges
- Optimize maintenance strategies and increase equipment availability operational output
- Predict asset integrity and reliability needs and improve time on tools
- Mitigate risks through stronger stakeholder partnerships, while removing redundancies in the supply chain
- Overcoming cultural and communication issues with contractors, while ensuring quality expectations
Do you want to understand how prepared your company is to drive needed asset performance and reliability improvements and what the key focus areas that will contribute to lower operating costs?
Want to find out more about how USC can help you uncover the hidden value lurking in asset portfolio?
For more information, let’s talk it through with a no obligation video conference call or a meeting with one of our executive team. Email info@usccg.com to arrange a call.
From supply chain disruptions to fluctuating demand, the past few years have caused a ripple-like wave of challenges throughout businesses across the globe, including the oil and gas industry.
Fortunately, with oil prices bouncing back, the oil and gas industry has nearly recovered from the issues to pre-COVID operations. That being said, there are a considerable number of concerns on the forefront of the industry that will shape the course of operations for years to come.
So, what’s the state of the oil and gas industry today? Let’s look at some of the issues and opportunities they’re facing.
Production capacity concerns
For months, we’ve been seeing news reports about the Russia and Ukraine conflict. Many of us have been seeking updates on the conflict itself, but those in the oil and gas industry have no doubt kept a keen eye on how it is affecting the global oil and gas market.
The sanctions placed on Russian oil have caused strain on a U.S. refinery system that, like so many manufacturing industries, was already overwhelmed and under-staffed following the COVID pandemic and the Great Resignation that followed. Demand for gas plummeted during a time when the majority of the country stayed in their homes for months on end, which left a large number of refineries with no other choice but to close their doors.
Refinery numbers still have not yet rebounded, which has resulted in a refining shortage of roughly one million barrels of oil a day compared to pre-COVID numbers. Add in sanctioning one of the world’s biggest oil producers, and the increased demand coupled with reduced refining capabilities combines into the perfect storm for shortages and increased prices.
Mergers & acquisitions opportunities
Despite the recently tabled climate bill, this country (and the world at large) is moving toward a renewable energy future. Even if it’s at a snail’s pace.
This has caused leaders in the oil and gas industry to evaluate operations and find ways to meet renewable and decarbonization efforts in the next few decades. One option is partnering with or purchasing renewable energy companies.
Companies like BP, Equinor, Respol, and PKN Orlen are leading the charge in renewable energy investment opportunities, and are reaping the financial and ecological rewards of doing so. Expect many major players in the oil and gas industry to continue to expand their portfolios and increase their outreach with strategic mergers and acquisitions into renewable energy.

Appeasement of investors
Despite incredible year-over-year growth, the oil and gas industry as a whole has been plagued with cash flow issues that have caused investors to reconsider their financial plans.
There are a host of reasons why investors have turned their focus toward other industries in recent years: Some have been leaving due to increased concerns over carbon-mitigation and ecological issues, some have left due to oil and gas’s tendency to overspend cash flows in the name of company growth and continued investment, while others have been scared away due to plain uncertainty.
Whatever the case may be, oil and gas companies are seeking to attract investors again, while investors want to see predictability and consistent returns to shareholders. The aforementioned increase in renewable mergers and acquisitions opportunities is a step in the right direction for the oil and gas industry, and that coupled with an inevitable stabilization will no doubt cause investors to flock back to the industry.
Outdated infrastructure & opportunity for innovation
Across the board, oil and gas infrastructure is aging.
In the off-shore sector, oil platforms are becoming old, deteriorated and increasingly at-risk for operational failures and natural disasters. This, of course, poses a problem not only for oil and gas companies meeting the ever-growing demand of the marketplace, but also risks ecological disaster in the form of oil spills and other malfunctions. Equipment and structural deterioration is no doubt due to saltwater and other environmental factors that come with operating in the ocean, and improvements to such facilities come at great expense, leaving some executives to employ a “we’ll-fix-it-when-it’s-broken” approach.
On land, plants and refineries across the country are aging, too, with many having outdated control loops, absences of updating engineering controls, and lack of complete computerization. This, of course, doesn’t even touch on the efficiency potential that technological aspects like robotic automation, artificial intelligence and IoT advances could bring to these facilities.
We can help
No matter the challenges, issues or opportunities facing the oil and gas industry, one solution is getting the job done more efficiently. That means looking at supply issues in new ways, casting an eye toward structural improvements and ensuring your day-to-day efficiency in the refineries and out in the field. We can help with that. At USC Consulting, we’ve been working with companies in a wide range of industries to up their efficiency game for more than 50 years.
Contact us today if you’d like to talk about how we can help your business.
As a typical rule of thumb in maintenance, planned work will consume roughly one third of the resources (labor cost, materials cost, and costs associated with equipment down-time) as unplanned work will consume. Therefore, the first objective of any maintenance program can be simplified as maximizing the percentage of time and resources spent on planned maintenance, and reducing the amount of unplanned maintenance or repair work resulting from unexpected breakdowns.
Understanding the Types of Work
Planned work can be broken down into two main categories: preventative maintenance and planned repairs. Preventative maintenance includes all the work done not in response to a failure, but to prevent future failures from occurring. This work is typically outlined by the manufacturer in terms of frequency and work that must be performed (oil change, lube, and filter). If the fleet size remains constant, so will the level of preventative maintenance. Planned repairs are work that must be done as a result of wear and tear in which the equipment has not yet failed and can still run reliably until the maintenance department is set up with the required materials, labor, and shop space to adequately address these repairs. For exemplary purposes in this article, we will consider maintenance needed for an underground mine as a model. Due to the travel time in underground mining and the requirement in most cases to have repairs done in the shop after a wash, these two types of planned work are best done together to minimize the mechanic’s trips to and from the equipment.
Given that the level of preventative maintenance will remain considerably flat, as both the materials required and time required can be predicted and cyclical, the only way to effectively increase planned work as a proportion of total work is to increase the level of planned repairs. The first task is to shift the balance of planned maintenance and unplanned maintenance. That is, to convert as much of the resources spent on unplanned work as possible into resources spent on planned work.

Converting Unplanned Work into Planned Maintenance
The first step is to create a backlog, a master list of all known repairs that must be made to each piece of equipment. It consists of repairs necessary to components that are in a partial state of failure, but have not yet failed. The size of a backlog and how well it is managed will provide some valuable insight as to the over-all health of your assets. A complete detailed backlog will also provide other benefits to management when taking a closer look at each type of equipment and analyzing which components require more attention than others. If repairs to equipment must be done before the equipment actually fails, the ability to identify or predict failures before they actually occur will be crucial. Coordination can then be made for the replacement of these components before failure occurs. This can be a very difficult and daunting task when considering a large fleet with complex equipment.
The first element to be considered when creating and managing a backlog is where the backlog work will be sourced from. Where will the maintenance planners get the information to create backlog list? Each time the equipment is inspected, an opportunity is provided to gather backlog. In an underground mining environment, some of these touch points include the preventative maintenance services, planned repairs, and operator circle checks.
An additional inspection can be strategically added to generate a greater and more detailed amount of backlog. Figure 1 below depicts the impact on parts procurement time of an inspection conducted by a mechanic in a predetermined time frame before the equipment is scheduled to come into the shop for a preventative maintenance service.
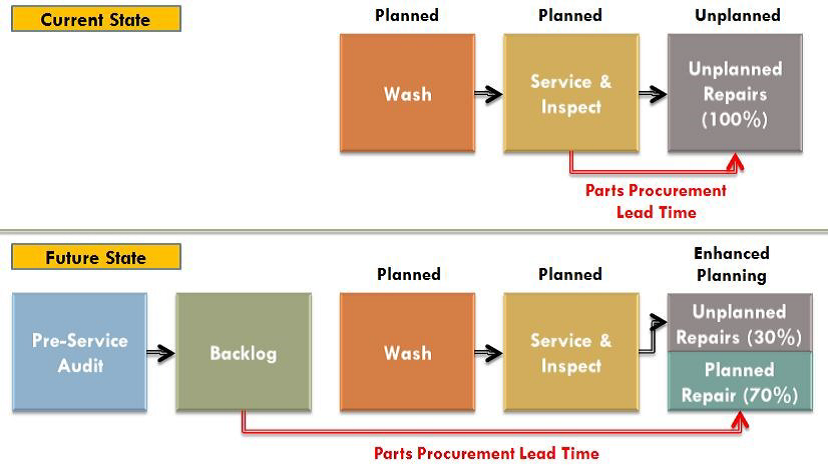
Figure 1—Current State vs. Future State with Backlog
Once the backlog list has been developed, the repairs can then be strategically scheduled alongside the preventative maintenance services while the equipment is already in the shop with shop space and labor assigned to it. Additionally, once these repairs have been scheduled, parts and materials can be ordered, packaged, and delivered to the shop where the repairs will be completed.
The supply benefits of planning repairs before failure are amplified in underground mining as the remote locations can be difficult for suppliers to deliver to. Even once on site, the materials must go through a complex supply delivery system to make their way underground. Planning these repairs ahead of time allows the equipment to run for the duration of this prolonged lead time. If the equipment is run until failure, it will remain down for the entire duration of this lead time until the needed parts can be delivered.
In generating and completing the backlog list against each piece of equipment, failures and breakdowns that would normally occur can now be discovered before failure and repaired on average much quicker than if the equipment would have broken down. The backlog system is working towards converting unplanned maintenance work into planned maintenance work, and therefore consuming one third of the resources on each repair converted as would normally be expended.
Planned maintenance leads to significant cost savings with improved productivity. For 50 plus years USC Consulting Group has helped organizations develop planned maintenance programs to increase their uptime. Contact us today to start converting your maintenance practices and keep your operations running as much as possible.
Heavy production assets are ubiquitous across numerous industries, from residential construction to mining. Keeping this mission-critical equipment up and running is among the top priorities for modern industrial organizations. It is why the average firm devotes almost 10 percent of its facilities budget to maintenance activities, according to researchers from Plant Engineering.
Virtually all of these entities leverage either predictive or preventive maintenance methodologies, both of which materialized in recent years due to widespread enterprise digitization. But how exactly are businesses deploying these strategies to ensure heavy production assets maintain peak performance? Here is an industry-agnostic look into the state of predictive and preventive maintenance best practices for heavy asset optimization:
Unpacking the preventive approach
An estimated 80 percent of maintenance teams employ preventive maintenance techniques, per survey data from Advanced Technology Services and Plan Engineering. The proactive approach centers on one operational goal: reducing production downtime. There are several associated best practices that guide preventive maintenance implementation and management.
Relinquishing the reactive approach to asset maintenance is the most impactful of these exercises. Unfortunately, it is also the hardest to adopt, Modern Materials Handling reported. Maintenance specialists that have traditionally listened for the cacophony of mechanical collapse and responded in turn must change their mindsets and instead focus on implementing piecemeal adjustments to mitigate the wear and tear that causes asset failure.
Making this cultural switch is no easy task – neither is reassessing all production and maintenance policies and procedures, and drafting new ones to comport with key performance indicators and company goals. However, four-fifths of maintenance teams have managed to execute these and the other preventive best practices on the way to transformation, including groups responsible for overseeing heavy assets.
Industrial organizations that excel at heavy machinery maintenance and effectively address small mechanical errors before they devolve into downtime-causing kinks focus on developing and sustaining routine asset optimization schedules, according to Reliable Plant. Through consistent check-ups and slight tweaks, maintenance teams responsible for bulky equipment can ensure these key production tools are always in good condition and ready to perform. Usage monitoring is also key, as heavy assets that are misused, either intentionally or unintentionally, typically break down the fastest.
How does usage monitoring unfold within an actual production workflow? A construction company preparing to excavate a new worksite might assess the climate and the soil to determine which backhoe digging attachment is not only best suited for the task at hand, but also the least likely to cause mechanical stress. These and other techniques make preventive maintenance possible, even with heavy assets in play.
Unpacking the predictive approach
When investments in heavy machinery began climbing dramatically more than a half decade ago, equipment manufacturers advised industrial companies to adopt asset tracking solutions to ensure that the multimillion-dollar tools they were deploying were actually required, The Wall Street Journal reported. At the same time, an innovative approach to maintenance, which also happened to be based on data analytics, was emerging.
This methodology, called predictive maintenance, would allow organizations to harness the power of advanced information technology to monitor mission-critical machinery in real-time, calculate the potential for future downtime and make improvements to avoid shutdown. In the years since this strategy materialized, many businesses have embraced it. In fact, 47 percent of industrial firms attest to deploying predictive maintenance processes and tools, per Advanced Technology Services and Plan Engineering.
Perhaps the most well-publicized and successful predictive maintenance programs have unfolded within organizations leveraging larger production assets. For example, construction equipment giant Caterpillar was among the first asset producers to manufacture products meant for use in predictive maintenance workflows, Forbes Magazine reported. The company began building bulldozers, dump trucks, excavators and other common equipment with pre-installed wireless sensors designed to transmit usable performance insights to maintenance leaders. Caterpillar customers have seen significant efficiency gains and cost reductions as a consequence of this forward-thinking equipment and the accompanying software.
Harley-Davidson is another early adopter that propelled predictive maintenance to new heights. Starting back in 2010, the automotive giant began outfitting the decades-old equipment in its York, Pennsylvania plant with wireless sensors configured to monitor mechanical operations and measure physical variables such as component vibration to assess asset performance, The Journal reported. These tools and the predictive maintenance program they facilitated led to drastic shop floor improvement, as Harley-Davidson watched production throughput times and costs decrease.
While impressive, these outcomes merely represent the initial stages of the predictive maintenance approach, according to PricewaterhouseCoopers. The rise of deployable enterprise artificial intelligence technology is expected to have an immense impact on this strategy, lending industrial firms the ability to monitor more data points across larger pools of equipment, including heavy assets.
That said, there is ample ground to cover before AI-propelled predictive maintenance workflows become industry standard. Most organizations inhabit the second position on the predictive maturity scale, per PwC, and therefore still depend on instrument inspections and other manual means. However, a significant number have entered stage three and now leverage real-time condition monitoring tools. Far fewer are in stage four, where expansive data-driven workflows capable of handling massive amounts of asset information are the norm.
In any case, predictive maintenance holds immense potential for teams assigned to heavy assets and, as the survey data from Advanced Technology Services and Plan Engineering indicates, a good number of the teams overseeing large machinery today have at least embraced some processes and tools associated with the strategy.
Implementing preventive and predictive maintenance strategies centered on heavy equipment can seem like an overwhelming task, especially for smaller industrial firms or those with particularly intense production demands. For businesses in these positions, external assistance could be all but necessary. USC Consulting Group has been helping organizations optimize their maintenance operations for decades, leveraging proven techniques and tools that accelerate change and lay the foundation for sustainable growth.
Connect with us today to learn more about our work and how we can help your company reduce heavy asset-related downtime.