-
Subscribe to Blog:
SEARCH THE BLOG
CATEGORIES
- Aerospace
- Asset Maintenance
- Automotive
- Blog
- Building Products
- Case Studies
- Chemical Processing
- Consulting
- Food & Beverage
- Forestry Products
- Hospitals & Healthcare
- Knowledge Transfer
- Lean Manufacturing
- Life Sciences
- Logistics
- Manufacturing
- Material Utilization
- Metals
- Mining
- News
- Office Politics
- Oil & Gas
- Plastics
- Private Equity
- Process Improvement
- Project Management
- Spend Management
- Supply Chain
- Uncategorized
- Utilities
- Whitepapers
BLOG ARCHIVES
- July 2025 (1)
- June 2025 (4)
- May 2025 (1)
- April 2025 (1)
- March 2025 (1)
- February 2025 (4)
- January 2025 (4)
- December 2024 (4)
- November 2024 (2)
- October 2024 (6)
- September 2024 (5)
- August 2024 (5)
- July 2024 (6)
- June 2024 (3)
- May 2024 (3)
- April 2024 (4)
- March 2024 (3)
- February 2024 (4)
- January 2024 (5)
- December 2023 (2)
- November 2023 (1)
- October 2023 (6)
- September 2023 (3)
- August 2023 (4)
- July 2023 (2)
- June 2023 (3)
- May 2023 (7)
- April 2023 (3)
- March 2023 (3)
- February 2023 (5)
- January 2023 (6)
- December 2022 (2)
- November 2022 (5)
- October 2022 (5)
- September 2022 (5)
- August 2022 (6)
- July 2022 (3)
- June 2022 (4)
- May 2022 (5)
- April 2022 (3)
- March 2022 (5)
- February 2022 (4)
- January 2022 (7)
- December 2021 (3)
- November 2021 (5)
- October 2021 (3)
- September 2021 (2)
- August 2021 (6)
- July 2021 (2)
- June 2021 (10)
- May 2021 (4)
- April 2021 (5)
- March 2021 (5)
- February 2021 (3)
- January 2021 (4)
- December 2020 (3)
- November 2020 (3)
- October 2020 (3)
- September 2020 (3)
- August 2020 (4)
- July 2020 (3)
- June 2020 (5)
- May 2020 (3)
- April 2020 (3)
- March 2020 (4)
- February 2020 (4)
- January 2020 (4)
- December 2019 (3)
- November 2019 (2)
- October 2019 (4)
- September 2019 (2)
- August 2019 (4)
- July 2019 (3)
- June 2019 (4)
- May 2019 (2)
- April 2019 (4)
- March 2019 (4)
- February 2019 (5)
- January 2019 (5)
- December 2018 (2)
- November 2018 (2)
- October 2018 (5)
- September 2018 (4)
- August 2018 (3)
- July 2018 (2)
- June 2018 (4)
- May 2018 (3)
- April 2018 (3)
- March 2018 (2)
- February 2018 (2)
- January 2018 (1)
- December 2017 (1)
- November 2017 (2)
- October 2017 (2)
- September 2017 (1)
- August 2017 (2)
- July 2017 (2)
- June 2017 (1)
- April 2017 (3)
- March 2017 (3)
- February 2017 (2)
- January 2017 (2)
- December 2016 (2)
- November 2016 (4)
- October 2016 (4)
- September 2016 (3)
- August 2016 (6)
- July 2016 (4)
- June 2016 (4)
- May 2016 (1)
- April 2016 (3)
- March 2016 (4)
- February 2016 (2)
- January 2016 (4)
- December 2015 (3)
- November 2015 (3)
- October 2015 (1)
- September 2015 (1)
- August 2015 (4)
- July 2015 (6)
- June 2015 (4)
- May 2015 (7)
- April 2015 (6)
- March 2015 (6)
- February 2015 (4)
- January 2015 (3)
CONNECT WITH US
Tag Archives: Downtime
Downtime – the dreaded halt in production that can cripple a manufacturing operation. It’s more than just an inconvenience; it’s a hidden cost that can eat away at your profits. A recent study revealed that nearly 82% of businesses have experienced unexpected downtime in the past three years, with the average incident lasting four hours and costing a staggering $2 million. The impact goes beyond just financial losses – downtime can disrupt customer deliveries, delay critical projects, and erode trust with clients.
The Potential Culprits
One major factor is neglecting preventive maintenance. Regular servicing not only keeps equipment functioning smoothly but also allows technicians to identify potential problems before they snowball into major breakdowns.
Another hidden source is outdated equipment. Obsolete machinery can be a drag on your entire production line. Imagine a slow, malfunctioning piece of equipment holding up the entire process. This can put undue stress on other machines, leading to premature wear and tear, and ultimately, more downtime. Upgrading to newer, more efficient models can significantly improve production flow and reduce the risk of breakdowns. Outdated software can also be a culprit. Running outdated software can lead to compatibility issues with newer systems and leave your facility vulnerable to security breaches.
Beyond equipment and software, a lack of proper training for your workforce can also contribute to downtime. If operators don’t fully understand how a machine works, they might misuse it, leading to errors and breakdowns. Investing in comprehensive training empowers your employees with the knowledge and skills they need to operate machinery safely and efficiently, minimizing the risk of operator-induced downtime.
Finally, the importance of data tracking cannot be overstated. Keeping detailed logs of equipment issues and production hiccups allows you to identify recurring problems and implement preventative measures. Think of it as a historical record that helps you anticipate and address potential bottlenecks before they derail your production schedule.
Finding the Right Solution for You
The good news is that there are steps you can take to combat downtime and keep your production lines humming. Conducting risk audits to identify potential problems, installing sensors to monitor equipment health (like a torque transducer that detects excessive force on a rotating shaft), and implementing a comprehensive preventive maintenance program are all crucial steps in the battle against downtime.
Investing in employee training and partnering with reliable third-party service providers can further strengthen your defenses. By adopting a proactive approach to maintenance and addressing the root causes of downtime, you can significantly reduce disruptions and ensure your manufacturing operation runs smoothly and efficiently.
Want to learn more about the specific costs associated with different downtime causes? The following infographic breaks down the financial impact of various downtime triggers, helping you identify areas for improvement and optimize your production process for maximum uptime.
In the dynamic realm of industrial operations, downtime is the arch-nemesis of productivity and profitability. Every minute lost to equipment breakdowns or maintenance activities translates into potential revenue losses, increased operating costs, and compromised competitiveness. Amidst this relentless pursuit of operational efficiency, the emergence of low or no maintenance industrial machinery heralds a transformative era for industries worldwide.
High maintenance equipment has long been a staple in industrial settings, requiring regular servicing, lubrication, and part replacements to ensure optimal performance. However, the inherent drawbacks of such machinery, including frequent downtime, escalating maintenance costs, and operational disruptions, have spurred a quest for alternative solutions.
Enter low or no maintenance industrial machinery—an innovation poised to revolutionize the industrial landscape. Engineered with durability, reliability, and longevity in mind, these advanced systems promise to mitigate the adverse effects of downtime and high maintenance requirements, ushering in a new era of seamless operations and cost savings.
The detrimental effects of downtime on industrial productivity cannot be overstated. Whether due to unexpected breakdowns or scheduled maintenance activities, every moment of idle machinery translates into lost production opportunities and diminished output. Moreover, the ripple effects of downtime extend beyond immediate financial implications, impacting supply chain dynamics, customer satisfaction, and overall business resilience.
In contrast, low or no maintenance components, equipment, and machinery offer a beacon of hope for industries grappling with the specter of downtime. By incorporating self-lubricating mechanisms, wear-resistant materials, and advanced monitoring technologies, these innovative solutions minimize the need for frequent maintenance interventions and extend operational uptime.
The benefits of adopting low or no maintenance industrial machinery are manifold. Beyond the immediate gains in productivity and cost savings, these systems promote a culture of efficiency, sustainability, and resilience within industrial ecosystems. By reducing reliance on traditional maintenance practices, industries can reallocate resources towards value-added endeavors, enhance worker safety, and contribute to environmental stewardship efforts.
In this infographic from FLEXIM, we delve into the profound impacts of downtime and high maintenance equipment on industrial operations, while illuminating the transformative potential of low or no maintenance machinery. Through compelling visuals and insightful analyses, we aim to empower industries with the knowledge and tools needed to navigate the evolving landscape of industrial maintenance and usher in a new era of efficiency and prosperity.
To learn more about best practices for asset management and reducing downtime, contact us to connect with our subject matter experts.
Manufacturers today deal with greater demands from consumers than ever before. It is vital for manufacturers to deliver on time, every time. Fail to do so and they will lose customers, revenue, and credibility.
Therefore, streamlining operations is essential. This doesn’t mean manufacturers need to invest in expensive equipment or high-performance technology. Often, what needs to change is how people work and the strategies businesses can employ to support this.
Let’s get started.
Why is it so Important to Streamline Manufacturing Operations?
Streamlining manufacturing processes ultimately maximizes a company’s profits and helps them stay competitive. Here are just some of the reasons why it’s so important:
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: streamlining manufacturing operations ensures that customer orders are received and fulfilled faster. Providing great customer service endears your company to your customers and keeps them loyal for the long-term.
- Cost-Effectiveness: every business wants to save money and streamlining operations is one of the best ways to achieve this. A streamlined manufacturing process requires less labor and significantly reduces time spent troubleshooting errors. This leaves more time (and money) for the things that are important – like better meeting customers’ needs.
- More Efficient Work Flow: when you have a streamlined manufacturing process, you have typically ironed out issues and eliminated bottlenecks that were causing delays. This improves the manufacturing process and results in a more efficient workflow. It enables manufacturers to produce goods faster, meet customers’ requests sooner, and achieve all of this without compromising on the quality of the product.
6 Ways Manufacturers Can Streamline Operations
Streamlining operations can feel like an overwhelming task at first. However, with the right strategies in place, it doesn’t take long to improve efficiency and boost productivity. Here are six tips to get you started:
1. Identify Issues in the Production Line
Every manufacturing operation has a bottleneck. This is a stage in the manufacturing process where things slow down or perhaps even stop. Bottlenecks are a nuisance and can lead to severe delays, time and labor inefficiencies, and increased costs. Identifying bottlenecks is essential for optimizing the production line and helping everything run more efficiently.
There are a few ways you can identify issues in your production line. For instance, you should look for signs of the following:
- Long wait times: if there are long wait times for customers or work is delayed because you’re waiting for materials or products to be delivered, this can cause bottlenecks and should be addressed as soon as possible.
- Backlogged work: you may also discover areas in your process where work is backlogged and piling up, causing a bottleneck that is harming your manufacturing efficiency. Taking care of backlogged work as a priority will help relieve these bottlenecks and get your process back up and running again.
- Machine Issues: sometimes machines fail and this could be due to lack of maintenance, outdated equipment, or poor staff training. Identifying machine issues and fixing these can have a huge impact on operation efficiency.
2. Support Faster Payment Processing
As a business owner, you know the importance of faster payment processing. Whether you’re paying your suppliers or your customers are buying your products, faster payment processing keeps everything running smoothly.
The simpler your payment process is, the better so spend time to find the best card reader for your business operation. Streamlining both the supplier and customer experience by offering online payments is a game-changer.
Online payments make it easier for customers to purchase from you, removing delays in the payment process and reducing cash flow issues. This helps streamline operations and keep everything running smoothly.
3. Adopt Lean Manufacturing Methodology
Lean manufacturing methodology focuses on reducing costs by limiting waste and improving manufacturing efficiency. Lean manufacturing is a great methodology to apply to your business if you’re looking to streamline operations.
For lean manufacturing methodology to be effective, all types of waste in the manufacturing process must be identified and then removed. There are four types of waste you should focus on eliminating as a priority. These include:
- Unnecessary transportation of materials such as equipment, tools, and employees can be avoided simply by optimizing factory layouts.
- Excess inventory. Whether it’s products, materials, or equipment, having excess inventory is a waste as it increases storage costs and slows down processes.
- Waiting time: time-wasting is common in manufacturing operations, either due to idle workers or idle machines. It typically occurs when workers can’t work because they’re waiting on materials or equipment. Machines can be idle when waiting on maintenance or replacement. Optimizing manufacturing processes eliminates this time wasting and boosts operational efficiency.
- Defective products are a waste that must be reduced as much as possible. For every defective product, you have an unhappy customer. This means returns are made and apologies are required, which increases costs and wastes time.
Reducing unnecessary waste goes a long way towards reducing lead times, boosting customer satisfaction, and improving operational efficiency. It is a process of continuous improvement and manufacturers will find that regular adjustments need to be made as customer demand fluctuates. However, adopting the lean manufacturing approach will go a long way towards streamlining your operations now and in the future.
4. Embrace Automation
Automation (utilizing production management software or robots to operate machinery) reduces the need for manual labor. It avoids human error and allows for consistency across all aspects of your manufacturing process.
Many areas within manufacturing can benefit from automation, most notably: payment and accounting processes, order processing, marketing efforts, and inventory management (to name a few!)
According to Industrial Machinery Digest, “One obvious byproduct of automation is increased productivity […] The market should see more businesses turning to industrial automation on various scales. When this happens, the market will be able to see not only more innovative products produced on a larger and quicker scale, but the quality increasing with production speed.”
Adopting automation as part of your manufacturing process will help streamline your operations like nothing else. It will allow your organization to keep up with customer demands and grow as your business grows.
5. Reduce Downtime (where possible)
As mentioned earlier in this article, many things can cause your processes to bottleneck. One of these is downtime.
Downtime is a significant cause of inefficiency in the manufacturing process. Therefore, finding ways to reduce it can improve efficiency. A few common causes of downtime are:
- Machine maintenance requirements
- Equipment failure
- Employee absenteeism
- Bottlenecks in the process
- Human error
To improve on these it is important to monitor your production processes closely. This will let you identify and address any issues quickly and efficiently.
6. Train Employees Well
For employees to do a good job and support a streamlined manufacturing process, they need to know what they’re doing and proper training supports this. Proper employee training is a surefire way to improve efficiency, boost company morale, and support business success.
Establishing an effective team through professional training lets employees add real value to your business by preparing them for higher responsibilities, increasing their productivity, strengthening any weaknesses, improving workplace safety, and boosting production overall.
If you want to streamline your manufacturing operations, it is essential that you properly train your employees. This will go a long way towards supporting your business success.
In Summary
We hope the tips shared in this article have highlighted the importance of optimizing your manufacturing processes and how to achieve this! We know that streamlining your operations can feel a little daunting at first (we’ve all been there!) But with the right strategies we know you can transform your manufacturing process and take your business to new heights.
*This article is written by Sophie Bishop. Sophie is an experienced construction writer with a passion for sharing insights and her experience within the health and safety sector. Sophie aims to spread awareness through her writing around issues to do with healthcare, wellbeing and sustainability within the industry and is looking to connect with an engaged audience. Contact Sophie via her website: https://sophiebishop.uk/.
The 2024 forecasts for the oil and gas industry include some conflicting speculation about supply and demand. It’s leading to confusion for U.S. companies… not to mention dismay as people everywhere scowl at the gas pump when they’re filling up.
Reuters reported in August that OPEC+ expects to see supply cuts that impact oil inventories, which will drive prices potentially higher than the $88 per barrel of crude in August 2023, the highest price since January. OPEC+ is confident, however, that demand will rise markedly.
But… the International Energy Association (IEA) doesn’t quite agree with those numbers, noting that the fluctuating economy will impact manufacturing businesses, and coupled with the tsunami of electric vehicles, will shake out in the form of falling demand.
Those clear-as-mud speculations boil down to one thing: Uncertainty is ahead for an industry that has already had its fair share.
All industries have been weathering uncertainty for the past few years, starting with the pandemic and, once we thought we had that handled, continuing with a shaky economy, a cried-wolf recession and ever-rising interest rates, putting consumer confidence on shifting sands.
At USC Consulting Group, we specialize in helping companies through uncertain times by optimizing their processes, becoming as efficient as possible and positioning themselves on solid ground to handle whatever is coming down the pike.
Preparing the Oil & Gas industry for an uncertain 2024
Here are seven ways the oil and gas industry can shore up for an uncertain 2024. Though separate goals, all work together to make companies as efficient and productive as they can be.
1. Reducing costs
Is there ever a year when companies in any industry shouldn’t focus on reducing costs? That’s a given, 24/7/365. But, it’s especially important for oil and gas going into 2024, when the economy continues to be volatile and uncertain. Buttoning up costs is a good strategy for the industry to get through that storm. It’s about optimizing production processes in the field and reducing extraction costs in order to offset costs involved in finding new sites.
2. Managing supply chain risks
After the supply chain bottlenecks most every industry experienced during the pandemic, it’s vital to mitigate supply chain risks. It’s a burr under the saddle of the entire industry. Fluctuating costs and supply uncertainty can impact the entire operation. Oil and gas companies need a little breathing room, predictable lead times and a more secure footing going into next year. Securing your supply chain is one way to achieve that. It can help avoid the market roller coaster we’ve seen in the recent past and may help ease pressure from inflation as well. The bonus here is, it can save about 15% on costs.
Developing a solid risk assessment plan that takes into consideration what’s happening at the supplier level will secure your supply chain and prevent any surprise shortages.
3. Focusing on yield
Maximizing yield, like reducing costs and managing supply chain risks, brings solid benefits in any economy, but especially now. It means making sure extraction techniques are as efficient as possible, utilizing methods like Enhanced Oil Recovery to extract more oil from reservoirs that may have been underutilized, managing those reservoirs carefully and by the numbers, and making sure employees across all facilities are on the same page.
4. Closing the how-why gap
In an organization the front line often does not understand the “why,” and the executives don’t understand the “how.” It means, the top brass do not fully understand how the job gets done and the frontline workers don’t fully understand why the job needs to be done. Closing that “how-why gap” is critical for optimal performance all the way up and down the organizational food chain.
5. Standardizing daily and weekly instructions for front-line managers
Going hand in hand with closing that how-why gap is increased training for managers. Many industries like oil and gas rely on frontline training, but some people would say that supervisors need even more. Training trickles down, but efficiency does, too. And the key to that is making sure everyone, across all departments and facilities, is on the same page, doing the job the same way, with a standard set of operating procedures. It’s a vital component for optimal efficiency.
6. Consolidation and acquisition = increased need for communication
New talent, ideas and perspectives can breathe life into a company. Mergers and acquisitions in the oil and gas industry exploded in Q2 2023, according to Enverus Intelligence Research. After $8 billion M&A in Q1 2023 (nothing to sneeze at) we saw $24b in Q2. It’s in line with increased consolidations, as reported by Forbes, with the goal of lowering costs, raising inventory and in the end, boosting investor returns.
All of that M&A activity can put a strain on employees of affected companies. Especially during this flurry of M&A, it’s important to find solutions to help them with the complexities of combining two “legacy” groups, which have their unique set of standards. Finding ways to combine both schools of thought into one set of “best practices” after a merger is paramount to its success. To learn more about it, read our recent case study: “Creating Harmony When Merging Two Companies.”
7. Performing scheduled maintenance
The goal is zero unplanned downtime. Pros in the industry know that’s not so easy to achieve. It starts with asset monitoring, including wells but also pipelines, processing facilities and other equipment to maximize operational efficiency. Scheduling downtime for maintenance ensures a shutdown, but it also ensures you’ll know when it’s coming and can plan accordingly. Unplanned failures or glitches can be costly problems at best but dangerous threats to workers at worst.
At USC Consulting Group, we’ve been working with the oil and gas industry for decades. If you’re interested in optimizing your company’s efficiency in this uncertain economy, give us a call.
Are you performing preventive maintenance on a regular basis? If you’re not, you may want to consider adding it to your schedule. Why? In a word, it’s about efficiency. In a few words (as its name suggests), it prevents problems before they start. Preventive maintenance is becoming the manufacturing industry standard. Roughly 80% of asset and facilities stakeholders are embracing the process as a way to cut costs, increase efficiency, and keep assets running like clockwork.
By performing regular preventive maintenance (or its cousin, data-based predictive maintenance) you are heading off problems, snafus and breakdowns at the pass. It’s about identifying and handling any potential issues that may be lurking down the road. The point is to find potential problems before they become real problems that could lead to delays and costly headaches.
The irony of preventive maintenance is that it can sometimes seem like it causes more problems than it solves. It requires regular downtime, which in itself is a problem. There’s also the tricky matter of timing. Finding the optimal time to perform the maintenance can be a delicate balance between shutting down for maintenance too soon and waiting too long.
But, the challenges are worth the rewards. Ensuring you have the proverbial well-oiled machine will make your operation more efficient and productive now and in the future.
Let’s take a look at preventive maintenance benefits and challenges and how it can help boost your operations.
Preventive maintenance benefits
The idea behind doing regular maintenance on the lifeblood of your manufacturing operations — your machinery — is to keep it humming along at optimal efficiency and prevent any problems that might occur. Benefits to making it a regular part of your business process include:
You control the downtime schedule. It’s true that performing maintenance requires downtime. You’ll experience a work stoppage because of it. However, the good news is, when that downtime happens is up to you. You can schedule it for slow periods and avoid your high-volume times. Build maintenance into your schedule as a regular part of your routine.
Fewer surprises. A snafu happens, something breaks, and you have to stop production to figure out what it is and fix it. That can happen at any time, and trust us, it will happen when you least want it to. Performing preventive, not reactive, maintenance will lessen those unwelcomed surprises that erode your productivity and profitability. A general rule is that planned work will cost two-thirds less than unplanned work in time and other resources.
Increased efficiency. At USC Consulting Group, we’re all about efficiency, and one of the surest ways to find “hidden efficiencies” that you didn’t even know were possible is to perform regular preventive maintenance on your machines.
Increased longevity of your machinery and assets. This is key. Just like your car needs regular oil changes and tune-ups to keep it running at its best, so do your assets.
Preventive maintenance challenges
There are some challenges with doing regular preventive maintenance. However, in our view, these don’t outweigh the benefits.
Finding the optimal time to do it is tricky. A regular schedule is the key to finding the best time to shut down for maintenance. And the downtime is typically where we see the most pushback from executives and managers who aren’t thrilled with this process.
It will cause shutdowns. There’s no way around it. To perform maintenance on your equipment, the line must stop.
If it ain’t broke, don’t fix it. This is an old adage for a reason. You may be shutting down for your scheduled maintenance when no problems actually exist. The shutdown does come at a productivity cost, so… is it worth it? Some manufacturers solve this issue by performing predictive maintenance instead. It’s a more complex process that is data driven, and analyzes how your assets are performing in real time. All’s well? No shutdown. But if you find problems, that’s when you act. It reduces downtime, and you’re not replacing any parts while they’re still good to go. The downside of this approach is complexity and connectivity. If you don’t have state-of-the-art machinery, you won’t get the data analytics that this process requires. That’s why the majority of manufacturers today are using the preventive approach.
At USC Consulting, we’ve been helping manufacturing businesses increase their efficiency, production, throughput and profits for more than half a century. Get in touch today if you’d like to learn more about how preventive maintenance benefits can boost your bottom line.
As a typical rule of thumb in maintenance, planned work will consume roughly one third of the resources (labor cost, materials cost, and costs associated with equipment down-time) as unplanned work will consume. Therefore, the first objective of any maintenance program can be simplified as maximizing the percentage of time and resources spent on planned maintenance, and reducing the amount of unplanned maintenance or repair work resulting from unexpected breakdowns.
Understanding the Types of Work
Planned work can be broken down into two main categories: preventative maintenance and planned repairs. Preventative maintenance includes all the work done not in response to a failure, but to prevent future failures from occurring. This work is typically outlined by the manufacturer in terms of frequency and work that must be performed (oil change, lube, and filter). If the fleet size remains constant, so will the level of preventative maintenance. Planned repairs are work that must be done as a result of wear and tear in which the equipment has not yet failed and can still run reliably until the maintenance department is set up with the required materials, labor, and shop space to adequately address these repairs. For exemplary purposes in this article, we will consider maintenance needed for an underground mine as a model. Due to the travel time in underground mining and the requirement in most cases to have repairs done in the shop after a wash, these two types of planned work are best done together to minimize the mechanic’s trips to and from the equipment.
Given that the level of preventative maintenance will remain considerably flat, as both the materials required and time required can be predicted and cyclical, the only way to effectively increase planned work as a proportion of total work is to increase the level of planned repairs. The first task is to shift the balance of planned maintenance and unplanned maintenance. That is, to convert as much of the resources spent on unplanned work as possible into resources spent on planned work.

Converting Unplanned Work into Planned Maintenance
The first step is to create a backlog, a master list of all known repairs that must be made to each piece of equipment. It consists of repairs necessary to components that are in a partial state of failure, but have not yet failed. The size of a backlog and how well it is managed will provide some valuable insight as to the over-all health of your assets. A complete detailed backlog will also provide other benefits to management when taking a closer look at each type of equipment and analyzing which components require more attention than others. If repairs to equipment must be done before the equipment actually fails, the ability to identify or predict failures before they actually occur will be crucial. Coordination can then be made for the replacement of these components before failure occurs. This can be a very difficult and daunting task when considering a large fleet with complex equipment.
The first element to be considered when creating and managing a backlog is where the backlog work will be sourced from. Where will the maintenance planners get the information to create backlog list? Each time the equipment is inspected, an opportunity is provided to gather backlog. In an underground mining environment, some of these touch points include the preventative maintenance services, planned repairs, and operator circle checks.
An additional inspection can be strategically added to generate a greater and more detailed amount of backlog. Figure 1 below depicts the impact on parts procurement time of an inspection conducted by a mechanic in a predetermined time frame before the equipment is scheduled to come into the shop for a preventative maintenance service.
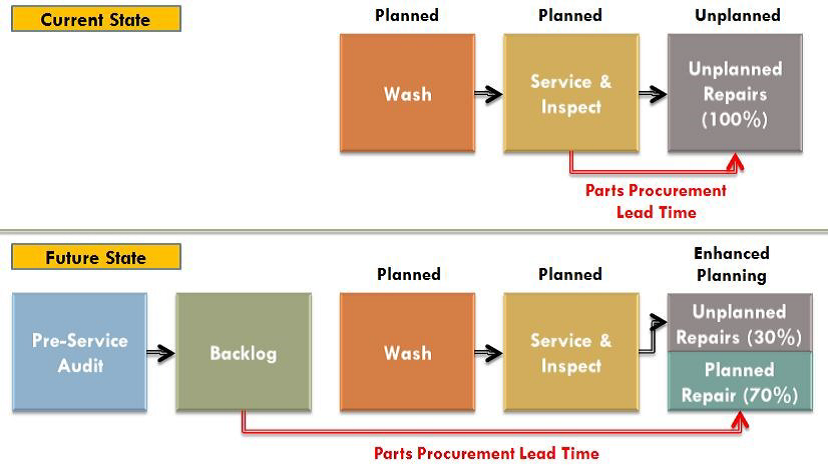
Figure 1—Current State vs. Future State with Backlog
Once the backlog list has been developed, the repairs can then be strategically scheduled alongside the preventative maintenance services while the equipment is already in the shop with shop space and labor assigned to it. Additionally, once these repairs have been scheduled, parts and materials can be ordered, packaged, and delivered to the shop where the repairs will be completed.
The supply benefits of planning repairs before failure are amplified in underground mining as the remote locations can be difficult for suppliers to deliver to. Even once on site, the materials must go through a complex supply delivery system to make their way underground. Planning these repairs ahead of time allows the equipment to run for the duration of this prolonged lead time. If the equipment is run until failure, it will remain down for the entire duration of this lead time until the needed parts can be delivered.
In generating and completing the backlog list against each piece of equipment, failures and breakdowns that would normally occur can now be discovered before failure and repaired on average much quicker than if the equipment would have broken down. The backlog system is working towards converting unplanned maintenance work into planned maintenance work, and therefore consuming one third of the resources on each repair converted as would normally be expended.
Planned maintenance leads to significant cost savings with improved productivity. For 50 plus years USC Consulting Group has helped organizations develop planned maintenance programs to increase their uptime. Contact us today to start converting your maintenance practices and keep your operations running as much as possible.
The U.S. chemicals manufacturing space is poised for growth following years of middling performance. Worldwide economic development, improvements in the domestic manufacturing and oil and gas industries, and the completion of improved chemical production infrastructure are likely to drive historic gains over the next two years, researchers from the American Chemistry Council found. Production volumes are expected to increase 3.7 percent in 2018 and 3.9 percent in 2019, laying the groundwork for an industrial valuation of more than $1 trillion by 2022. How has the sector managed to regain ground in the marketplace? Increased production capacity linked to digitization.
Advanced hardware and software are transforming chemicals producers of all sizes, facilitating efficiency gains across virtually all operational areas, from the back office to the shop floor, according to the World Economic Forum. By 2025, digital technology will have generated a cumulative economic value of between $310 billion and $550 billion within the worldwide chemicals space. There are, of course, countless solutions and deployment methods specially designed for use within the chemicals manufacturing arena. However, innovations centered on asset management stand above the rest in terms of demonstrable operational impact.
Unpacking the asset management equation
Chemical companies live and die by the mission-critical machinery they use to craft their product. In the event of unexpected downtime, the entire operation grinds to a halt, customers orders go unfilled, and revenue drops. Losses can increase at an accelerated rate when this occurs. For example, the average automotive manufacturer loses an estimated $22,000 per minute of unplanned production stoppage, according to research from Advanced Technology Services and Nielsen. Only the largest companies can weather such losses. Small or midsize organizations might falter entirely under the weight of such astronomical downtime costs.
Chemicals manufacturers are at great risk for suffering such events due to the very nature of their work. These firms supply the market with more than 100,000 different chemical compounds, according to the WEF. The vast majority of these substances are extremely caustic and therefore wreak havoc on production assets, requiring major investments in maintenance. In the U.S., chemicals producers are expected to spend more than $1.26 billion on planned maintenance activities in 2018, constituting a year-over-year rise of more than 38 percent, analysts for the ACC found. Of course, this figure does not take into account unplanned work, which usually costs 2 to 5 times more than scheduled activities, according to the Marshall Institute.
Implementing an innovative solution
Rising costs and the continual existence of massive maintenance-related risk has forced businesses in the chemicals manufacturing arena to embrace bleeding-edge technology in hopes of streamlining asset management workflows and ultimately improving reliability. Many are turning toward predictive maintenance processes powered by connected equipment sensors and robust backend platforms, Schneider Electric reported. These all-encompassing solutions allow chemical companies of all sizes to closely monitor their production assets and catch small mechanical issues before they devolve into full-on catastrophes with the potential to cause downtime. Such products also give producers the power to continually fine-tune their machinery, embrace continuous improvement, and boost productivity.
Early adopters have seen serious results, promoting wider investment in the technologies that underpin such proactive asset management approaches. For instance, businesses across all sectors are expected to spend more than $239 billion on industrial sensor technology alone in 2018, researchers for the International Data Corporation have predicted. Firms in the chemicals manufacturing space are likely to contribute to this spend as they retrofit their production workflows to more effectively compete in an expanding marketplace. However, such technology is unlikely to remain optional for long. Almost 90 percent of chemical company executives believe businesses in the industry that fail to embrace digitization will end up falling behind, the WEF found.
Chemicals manufacturing firms standing on the outside looking in on this trend must act quickly to implement next-generation asset management processes and technology. USC Consulting Group can help. Here at USCCG, we’ve been working with businesses across numerous industries for 50 years, helping them adjust to marketplace transformations of all kinds. Connect with us today to learn more about our work and how our chemicals manufacturing consultants can help your enterprise embrace and benefit from digitization.
Let’s keep in touch – subscribe to our blog in the top right of this page or follow us on LinkedIn and Facebook.
The American manufacturing space has experienced considerable improvement in recent years. Producers have embraced data-driven processes and procedures designed to boost productivity and keep overhead costs down. The industry contributed approximately $2.2 trillion to the U.S. gross domestic product in 2016, capping off four consecutive years of annual value-added figures above the $2 trillion mark, according to the Bureau of Economic Analysis. But this success is not a symptom of scale. More than 98 percent of U.S. manufacturing firms have fewer than 500 workers, according to the National Association of Manufacturers. More astonishingly, 3 out of 4 firms employ fewer than 20 workers.
How do American manufacturers account for more than 10 percent of the national GDP with such small staff rosters at their disposal? Operational optimization through continuous improvement. Almost 70 percent of domestic producers utilize lean manufacturing strategies to facilitate such an approach, Reliable Plant reported. These methodologies center on the collection and evaluation of key performance indicators, critical quality metrics that lend operational leaders insight into mission-critical workflows, giving them the power to spot deficiencies and make changes as quickly as possible. Only with this data can firms successfully navigate the modern marketplace where responsiveness reigns supreme.
There are numerous shop floor functions suitable for performance measurement programs. However, industry innovators and researchers have pinpointed several operational avenues that can provide data capable of driving continuous change and bolstering the bottom line. Here are some of the KPIs associated with these shop floor hotspots:
1. Total downtime
Downtime is a manufacturer’s greatest enemy. When mission-critical assets stop functioning because of mechanical issues, producers often lose hundreds of thousands of dollars. For example, automakers lose an average of $22,000 per minute of downtime, according to research from Advanced Technology Services. A large number of modern manufacturers can’t survive such losses as most are already operating on razor-thin profit margins. This state of affairs makes the total downtime KPI an essential metric of quality. Gathering this data is relatively easy, but tracking it and exploring the operational variables behind it can have an immense impact.
Most producers pair this macro measurement with finer KPIs, such as overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) or changeover time, to form a more robust downtime picture.
2. Takt time
This versatile KPI – the amount of time it takes to complete a given task – works in numerous operational contexts. According to Food Manufacturing, plant supervisors can leverage takt time to track the entire product creation process and monitor the smaller functions that make up this total workflow. This allows for increased visibility and gives producers the power to institute minor tweaks in piecemeal to get the most out of their shop floors. Takt time is also one of the few KPIs that relates directly to the customer. These readings can show businesses where they stand in relation to customer demands centered on timeliness, even reveal upgrades that could quicken production processes and more effectively meet the needs of modern buyers.
On the surface this KPI may seem basic, but its versatility and connection to the customer experience make it an essential metric for even the most advanced manufacturers. Again, there are other KPIs that work well with takt time, including estimated time to completion and piece variance. These measurements relate directly to customer satisfaction and can therefore yield useable insights with transformative power.
3. First pass yield
The days of the single-use production line are over. To compete in today’s marketplace, manufacturers must be prepared to reconfigure their operations to meet changing volume demands or roll out new products altogether. This state of affairs makes first pass yield an essential KPI for modern producers. This metric measures the effectiveness of a given workflow during its initial run. Quality assurance personnel calculate the first pass yield by dividing the number of completed units requiring no rework by the number of total products produced. Using this figure, shop floor stakeholders can assess the overall efficacy of a new process and make changes to improve its productivity.
In the past, this KPI may have been something manufacturing leaders used only occasionally. But times have changed. With customer demands shifting so frequently, manufacturers must be ready to reorganize their processes and measure their effectiveness after reorganization. The first pass yield KPI makes this possible.
4. Mean time between failures
Manufacturers are only as reliable as the production equipment they have on the shop floor. This is why many organizations adopt preventive maintenance strategies with cutting-edge technology at their centers. More than 40 percent of manufacturers currently subscribe to this approach, while another 30 percent have gone one step further and embraced predictive maintenance, according to recent research from Plant Services. A majority of these maintenance-minded firms rely on the KPI mean time between failures (MTBF), which is the length of time a repairable asset will function properly after experiencing a major mechanical problem and before doing so again. This KPI gives maintenance teams a base line off of which they can schedule preventive activities.
Mean time between failures and related metrics, such as mean time to failure (MTTF) and mean time to repair (MTTR), help manufacturers evaluate overall asset reliability. With this information in hand, operational stakeholders can make incremental improvements to plant efficiency and productivity.
Manufacturing businesses looking to carve out space in today’s marketplace must focus on continually improving their workflows, as processes, not manpower, lay the groundwork for success. These KPIs give such enterprises the power to dive deeply into their operations and pinpoint deficiencies big and small that could be holding them back. Here at USC Consulting Group, we have been working with manufacturers for decades, connecting them with experts who can craft customized operational improvement plans designed to stimulate growth. Contact us today to learn more about our work in the space and how our in-house consultants can help your firm reach new heights.










